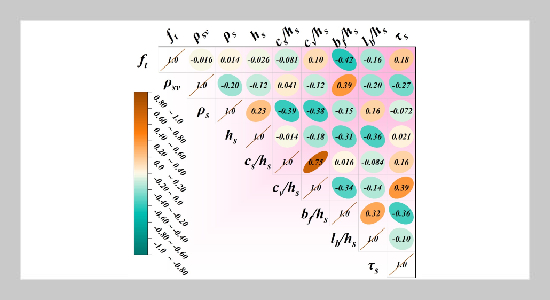
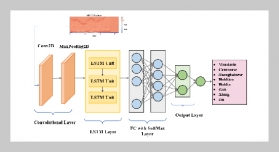
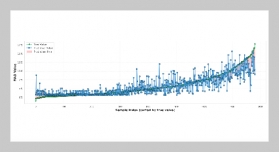
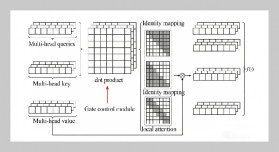
- [1] Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, H. Xin, and J. He, (2019) “Numerical parametric study on ultimate load and ductility of concrete encased equal-leg angle steel composite columns" Engineering structures 200: 109679. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109679.
- [2] B. Lai, J. Y. R. Liew, A. Venkateshwaran, S. Li, and M. Xiong, (2020) “Assessment of high-strength concrete encased steel composite columns subject to axial compression" Journal of constructional steel research 164: 105765. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2019.105765.
- [3] R. S. Benemaran, M. Esmaeili-Falak, and M. S. Kord lar, (2024) “Improvement of recycled aggregate concrete using glass fiber and silica fume" Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling, Experiments and Design 7: 1895–1914. DOI: 10.1007/s41939-023-00313-2.
- [4] X. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Lu, and X. Li, (2020) “Bond behavior and shear transfer of steel section-concrete interface with studs: Testing and modeling" Construction and Building Materials 264: 120251. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120251.
- [5] X.Wang,Y.Liu,F.Yang,Y.Lu,andX.Li,(2019)“Effect of concrete cover on the bond-slip behavior between steel section and concrete in SRC structures" Construction and Building Materials 229: 116855. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116855.
- [6] C. Zongping and Y. Wudang, (2016) “Push-out test on interface bond behavior between shape steel and high strength concrete and interfacial bond-slip constitutive relation" Journal of Building Structures 37: 150–157. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2016.02.019.
- [7] C. Liu, L. Xing, H. Liu, Z. Quan, G. Fu, J. Wu, Z. Lv, and C. Zhu, (2020) “Numerical study of bond slip between section steel and recycled aggregate concrete with full replacement ratio" Applied Sciences 10: 887. DOI: 10.3390/app10030887.
- [8] C. W. Roeder, R. Chmielowski, and C. B. Brown, (1999) “Shear connector requirements for embedded steel sections" Journal of Structural Engineering 125: 142–151. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1999)125:2(142).
- [9] M. Sato and S. Tanaka, (1993) “Bond strength of steel pipe and H-shape confined in concrete" Ann Collection Academic Papers Concrete Science 15: 183–186.
- [10] Z. Tao and Q. Yu, (2012) “Residual bond strength in steel reinforced concrete columns after fire exposure" Fire safety journal 53: 19–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2012.06.010.
- [11] Y. Majdi, C.-T. T. Hsu, and S. Punurai, (2014) “Local bond–slip behavior between cold-formed metal and concrete" Engineering structures 69: 271–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.03.025.
- [12] M.Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2024) “Ensemble extreme gradient boosting based models to predict the bearing capacity of micropile group" Applied Ocean Research 151: 104149. DOI: 10.1016/j.apor.2024.104149.
- [13] X. Sun, X. Dong, W. Teng, L. Wang, and E. Has sankhani, (2024) “Creation of regression analysis for estimation of carbon fiber reinforced polymer-steel bond strength" Steel and Composite Structures 51: 509. DOI: 10.12989/scs.2024.51.5.509.
- [14] K. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and B. Razzaghzadeh, (2024) “Application of the optimal fuzzy-based system on bearing capacity of concrete pile" Steel and Composite Structures 51: 25. DOI: 10.12989/scs.2024.51.1.025.
- [15] Y. Zhu, L. Huang, Z. Zhang, and B. Bayrami, (2022) “Estimation of splitting tensile strength of modified recycled aggregate concrete using hybrid algorithms" Steel and Composite Structures: 389–406. DOI: 10.12989/scs.2022.44.3.389.
- [16] Y. Dawei, Z. Bing, G. Bingbing, G. Xibo, and B. Razza ghzadeh, (2023) “Predicting the CPT-based pile set-up parameters using HHO-RF and PSO-RF hybrid mod els" Structural Engineering and Mechanics, An Int’l Journal 86: 673–686. DOI: 10.12989/sem.2023.86.5. 673.
- [17] R. Liang and B. Bayrami, (2022) “Estimation of frost durability of recycled aggregate concrete by hybridized Random Forests algorithms" Steel and Composite Structures: 91–107. DOI: 10.12989/scs.2023.49.1.091.
- [18] N.-D. Hoang, (2024) “Metaheuristic optimization of ex treme gradient boosting machine for enhanced prediction of lateral strength of reinforced concrete columns under cyclic loadings" Results in Engineering 24: 103125. DOI: 10.1016/j.rineng.2024.103125.
- [19] M. Esmaeili-Falak, H. Katebi, M. Vadiati, and J. Adamowski, (2019) “Predicting triaxial compressive strength and Young’s modulus of frozen sand using artificial intelligence methods" Journal of Cold Regions Engineering 33: 04019007. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.0000188.
- [20] M. Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2024) “Ap plication of optimization-based regression analysis for evaluation of frost durability of recycled aggregate concrete" Structural Concrete 25: 716–737. DOI: 10.1002/suco.202300566.
- [21] D. Li, X. Zhang, Q. Kang, and E. Tavakkol, (2023) “Estimation of unconfined compressive strength of marine clay modified with recycled tiles using hybridized extreme gradient boosting method" Construction and Building Materials 393: 131992. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131992.
- [22] H. Kou, J. Quan, S. Guo, and E. Hassankhani, (2024) “Light and normal weight concretes shear strength estimation using tree-based tunned frameworks" Construction and Building Materials 452: 138955. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.138955.
- [23] R. S. Benemaran, (2023) “Application of extreme gradient boosting method for evaluating the properties of episodic failure of borehole breakout" Geoenergy Science and Engineering 226: 211837. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211837.
- [24] B. M. Yaychi and M. Esmaeili-Falak, (2024) “Estimating axial bearing capacity of driven piles using tuned random forest frameworks" Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 42: 7813–7834. DOI: 10.1007/s10706-024-02952-9.
- [25] E. M. Golafshani, A. Rahai, M. H. Sebt, and H. Ak barpour, (2012) “Prediction of bond strength of spliced steel bars in concrete using artificial neural network and fuzzy logic" Construction and building materials 36: 411–418. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.04.046.
- [26] H.-J. Hwang, J.-W. Baek, J.-Y. Kim, and C.-S. Kim, (2019) “Prediction of bond performance of tension lap splices using artificial neural networks" Engineering Structures 198: 109535. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109535.
- [27] Z. M. Yaseen, B. Keshtegar, H.-J. Hwang, and M. L. Nehdi, (2019) “Predicting reinforcing bar development length using polynomial chaos expansions" Engineering Structures 195: 524–535. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct. 2019.06.012.
- [28] Ł.SadowskiandJ.Hoła,(2015)“ANNmodelingofpull off adhesion of concrete layers" Advances in Engineering Software 89: 17–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.06.013.
- [29] R. HaddadandM.Haddad,(2021) “Predicting fiber reinforced polymer–concrete bond strength using artificial neural networks: A comparative analysis study" Structural Concrete 22: 38–49. DOI: 10.1002/suco.201900298.
- [30] W.B. Chaabene, (2020) “Machine Learning Prediction of Shear Capacity of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete":
- [31] J. Kennedy and R. Eberhart. “Particle swarm optimization”. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95-international conference on neural networks. 4. ieee, 1995, 1942–1948. DOI: 10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968.
- [32] N.-D. Hoang, (2024) “Metaheuristic optimization of extreme gradient boosting machine for enhanced prediction of lateral strength of reinforced concrete columns under cyclic loadings" Results in Engineering 24: 103125. DOI: 10.1016/j.rineng.2024.103125.
- [33] X. Wang, Y. Liu, F. Yang, Y. Lu, and X. Li,(2019)“Effect of concrete cover on the bond-slip behavior between steel section and concrete in SRC structures" Construction and Building Materials 229: 116855. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116855.
- [34] C. Liu, L. Xing, H. Liu, Z. Quan, G. Fu, J. Wu, Z. Lv, and C. Zhu, (2020) “Numerical study of bond slip between section steel and recycled aggregate concrete with full replacement ratio" Applied Sciences 10: 887. DOI: 10.3390/app10030887.
- [35] H. Zheng, Z. Chen, and J. Xu, (2016) “Bond behavior of H-shaped steel embedded in recycled aggregate concrete under push-out loads" International Journal of Steel Structures 16: 347–360. DOI: 10.1007/s13296-016 6008-y.
- [36] B. Liu, G.-L. Bai, and Z.-Z. Wang, (2021) “The bond stress-slip full curve equation between the RAC and H shaped: Experimental, theoretical and numerical simulation investigation" Construction and Building Mate rials 311: 125311. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125311.
- [37] R. Ren, L. Qi, J. Xue, and X. Zhang, (2020) “Cyclic bond property of steel reinforced recycled concrete (SRRC) composite structure" Construction and Building Materials 245: 118435. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118435.
- [38] C. Liu, Z. Lv, G. Bai, and Y. Yin, (2018) “Experiment study on bond slip behavior between section steel and RAC in SRRC structures" Construction and Building Materials 175: 104–114. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.120.
- [39] G. Z. Deng,(2004) “Experimental study and basic theory analysis on bond-slip behavior between steel shape and concrete in steel reinforced concrete structures" Civil Eng. Thesis, Xi’an University of Arc. & Tec., Xi’an, China:
- [40] C. Liu, Z. Fan, X. Chen, C. Zhu, H. Wang, and G. Bai, (2019) “Experimental study on bond behavior between section steel and RAC under full replacement ratio" KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 23: 1159–1170. DOI: 10.1007/s12205-019-0702-1.
- [41] J.Song,W.Wang,S.Su,X.Ding,Q.Luo,andC.Quan, (2020) “Experimental study on the bond-slip performance between concrete and a corrugated steel plate with studs" Engineering Structures 224: 111195. DOI: 10.1016/j. engstruct.2020.111195.
- [42] L. Bai, J. Yu, M. Zhang, and T. Zhou, (2019) “Experi mental study on the bond behavior between H-shaped steel and engineered cementitious composites" Construction and Building Materials 196: 214–232. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.117.
- [43] M. Ming, S. Zheng, Y. Zhang, Y. Zheng, S. Yang, and M.Song. “Experimental study on the bond-slip behavior and stress transfer mechanism between shaped steel and high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete”. In: Structures. 34. Elsevier, 2021, 5013–5028. DOI: 10.1016/j.istruc.2021.09.014.
- [44] C. Zongping and Y. Wudang, (2016) “Push-out test on interface bond behavior between shape steel and high strength concrete and interfacial bond-slip constitutive relation" Journal of Building Structures 37: 150–157. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2016.02.019.
- [45] W. Aribowo, (2023) “A novel improved sea-horse optimizer for tuning parameter power system stabilizer" Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC) 4: 12–22. DOI: 10.18196/jrc.v4i1.16445.
- [46] S. Zhao, T. Zhang, S. Ma, and M. Wang, (2023) “Sea horse optimizer: a novel nature-inspired meta-heuristic for global optimization problems" Applied Intelligence 53: 11833–11860. DOI: 10.1007/s10489-022-03994-3.
- [47] S. Zhao, T. Zhang, S. Ma, and M. Wang, (2023) “Sea horse optimizer: a novel nature-inspired meta-heuristic for global optimization problems" Applied Intelligence 53: 11833–11860. DOI: 10.1007/s10489-022-03994-3.
- [48] S. Talatahari and M.Azizi, (2020) “Optimization of con strained mathematical and engineering design problems using chaos game optimization" Computers & Indus trial Engineering 145: 106560. DOI: 10.1016/j.cie.2020.106560.
- [49] A. Dahou, S. A. Chelloug, M. Alduailij, and M. A. Elaziz, (2023) “Improved feature selection based on chaos game optimization for social internet of things with a novel deep learning model" Mathematics 11: 1032. DOI: 10.3390/math11041032.
- [50] V. Goodarzimehr, S. Talatahari, S. Shojaee, S. Hamzehei-Javaran, and P. Sareh, (2022) “Structural design with dynamic constraints using weighted chaos game optimization" Journal of Computational Design and Engineering 9: 2271–2296. DOI: 10.1093/jcde/qwac099.
- [51] S. Talatahari and M. Azizi, (2021) “Chaos game opti mization: a novel metaheuristic algorithm" Artificial Intelligence Review54: 917–1004. DOI: 10.1007/s10462-020-09867-w.
- [52] H. I. Erdal, (2013) “Two-level and hybrid ensembles of decision trees for high performance concrete compressive strength prediction" Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 26: 1689–1697. DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2013.03.014.
- [53] A. Ahmad, F. Farooq, P. Niewiadomski, K. Ostrowski, A. Akbar, F. Aslam, and R. Alyousef, (2021) “Prediction of compressive strength of fly ash based concrete using individual and ensemble algorithm" Materials 14: 794. DOI: 10.3390/ma14040794.
- [54] A. Karbassi, B. Mohebi, S. Rezaee, and P. Lestuzzi, (2014) “Damage prediction for regular reinforced concrete buildings using the decision tree algorithm" Computers &Structures 130: 46–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2013.10.006.
- [55] S. B. Kotsiantis, (2013) “Decision trees: a recent overview" Artificial Intelligence Review 39: 261–283. DOI: 10.1007/s10462-011-9272-4.
- [56] S. Zhang, J. Xu, T. Lai, Y. Yu, and W. Xiong, (2023) “Bond stress estimation of profiled steel-concrete in steel reinforced concrete composite structures using ensemble machine learning approaches" Engineering Structures 294: 116725. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2023.116725.