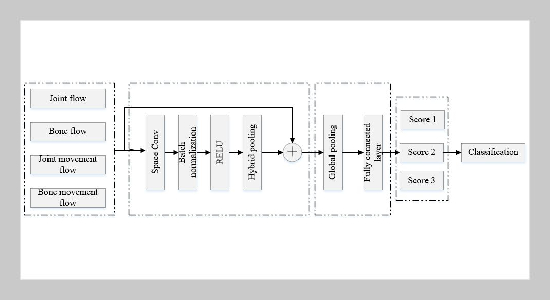
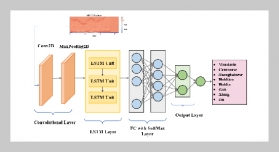
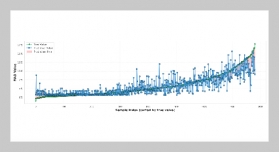
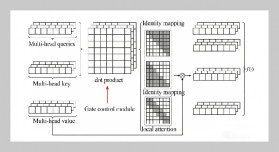
- [1] N.Manakitsa,G.S.Maraslidis,L.Moysis,andG.F. Fragulis, (2024) “Areviewofmachine learning and deep learning for object detection, semantic segmentation, and humanaction recognition in machine and roboticvision"Technologies12(2):15.DOI:10.3390/technologies12020015.
- [2] D.Guo,K.Li,B.Hu,Y.Zhang,andM.Wang,(2024) “Benchmarkingmicro-actionrecognition:Dataset,methods, and applications" IEEE Transactions on Circuits and SystemsforVideoTechnology34(7):6238–6252. DOI:10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3358415.
- [3] S. Yin, H. Li, A. A. Laghari, T. R. Gadekallu, G. A. Sampedro, andA.Almadhor, (2024)“Ananomaly detection model based on deep auto-encoder and capsule graph convolution via sparrow search algorithm in 6G Internet of Everything "IEEE Internet of Things Journal 11(18):29402–29411.DOI:10.1109/JIOT.2024.3353337.
- [4] M.AntounandD.Asmar,(2023)“Humanobjectinter action detection: Design and survey "Image and Vision Computing130:104617.DOI:10.1016/j.imavis.2022.104617.
- [5] H.Zhou,W.Zhou,Y.Zhou,andH.Li,(2021)“Spatial temporal multi-cuenet work for signlanguage recognition and translation"IEEE Transactionson Multimedia 24:768–779.DOI:10.1109/TMM.2021.3059098.
- [6] P.Ravbar,K.Branson,andJ.H.Simpson,(2019)“An automatic behavior recognition system classifies animal behaviors using movements and their temporal context" Journalofneurosciencemethods326:108352.DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.108352.
- [7] L. Pigou, A. Van Den Oord, S. Dieleman, M. Van Herreweghe,andJ.Dambre,(2018)“Beyondtemporal pooling: Recurrence and temporal convolutions for gesture recognition in video" International Journal of Computer Vision 126(2): 430–439. DOI: 10.1007/s11263 016-0957-7.
- [8] Y. Jiang and S. Yin, (2023) “Heterogenous-view occluded expression data recognition based on cycle-consistent adversarial network and K-SVD dictionary learning under intelligent cooperative robot environment" Computer Science and Information Systems 20(4): 1869–1883. DOI: 10.2298/CSIS221228034J.
- [9] Y. Zhou, X. Yan, Z.-Q. Cheng, Y. Yan, Q. Dai, and X.-S. Hua. “Blockgcn: Redefine topology awareness for skeleton-based action recognition”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024, 2049–2058. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00200.
- [10] Y. Abbas and A. Jalal. “Drone-based human action recognition for surveillance: a multi-feature ap proach”. In: 2024 International Conference on Engineering & Computing Technologies (ICECT). IEEE. 2024, 1 6. DOI: 10.1109/ICECT61618.2024.10581378.
- [11] Y. Ma and R. Wang, (2024) “Relative-position embed ding based spatially and temporally decoupled Trans former for action recognition" Pattern Recognition 145: 109905. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109905.
- [12] M. Munsif, N. Khan, A. Hussain, M. J. Kim, and S. W. Baik, (2024) “Darkness-adaptive action recognition: Leveraging efficient tubelet slow-fast network for industrial applications" IEEE Transactions on Indus trial Informatics 20(12): 13676–13686. DOI: 10.1109/ TII.2024.3431070.
- [13] I. A. Abro and A. Jalal. “Multi-Modal Sensors Fusion for Fall Detection and Action Recognition in Indoor Environment”. In: 2024 3rd International Conference on Emerging Trends in Electrical, Control, and Telecommu nication Engineering (ETECTE). IEEE. 2024, 1–6. DOI: 10.1109/ETECTE63967.2024.10823705.
- [14] N. Siddiqui, P. Tirupattur, and M. Shah. “DVANet: Disentangling view and action features for multi view action recognition”. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 38. 5. 2024, 4873 4881. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v38i5.28290.
- [15] S. Rakshit, T. Davies, M. M. Moradi, G. McSwiggan, G. Nair, J. Mateu, andA.Baddeley, (2019) “Fast kernel smoothing of point patterns on a large network using two-dimensional convolution" International Statistical Review 87(3): 531–556. DOI: 10.1111/insr.12327.
- [16] X. Ma, W. Xu, H.Guan, and X. Zhang, (2024) “Three dimensional image recognition of soybean canopy based on improved multi-view network" Industrial Crops and Products 222: 119544. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024. 119544.
- [17] Y. Zhang, J. Li, N. Jiang, G. Wu, H. Zhang, Z. Shi, Z. Liu, Z. Wu, and X. Liu, (2023) “Temporal transformer networks with self-supervision for action recognition" IEEE Internet of Things Journal 10(14): 12999–13011. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3257992.
- [18] S. Basak, P. Corcoran, R. McDonnell, and M. Schukat, (2022) “3D face-model reconstruction from a single image: A feature aggregation approach using hierarchical trans former with weak supervision" Neural Networks 156: 108–122. DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.09.019.
- [19] H.QiuandB.Hou,(2024) “Multi-grained clip focus for skeleton-based action recognition" Pattern Recognition 148: 110188. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.110188.
- [20] M.Batool, M. Alotaibi, S. R. Alotaibi, D. A. Al Hammadi, M. A. Jamal, A. Jalal, and B. Lee, (2024) “Multimodal human action recognition framework using an improved CNNGRU classifier" IEEE Access 12: 158388 158406. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3481631.
- [21] K. Peng, C. Yin, J. Zheng, R. Liu, D. Schneider, J. Zhang, K. Yang, M. S. Sarfraz, R. Stiefelhagen, and A. Roitberg. “Navigating open set scenarios for skeleton-based action recognition”. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 38. 5. 2024, 4487–4496. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v38i5.28247.
- [22] R. Xie, Y. Jiang, and J. Yu. “Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional network with multi-head attention mechanism for industrial safety detection”. In: Fifth International Conference on Telecommunications, Optics, and Computer Science (TOCS 2024). 13629. SPIE. 2025, 710–716. DOI: 10.1117/12.3067995.
- [23] Z. Bai, Q. Ding, H. Xu, J. Chi, X. Zhang, and T. Sun, (2022) “Skeleton-based similar action recognition through integrating the salient image feature into a center connected graph convolutional network" Neurocomputing 507: 40–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.07.080.
- [24] W. Hong, W. Xu, J. Qi, and Y. Weng, (2019) “Neural tensor network for multi-label classification" IEEE Ac cess 7: 96936–96941. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2930206.
- [25] L.Teng,Y. Qiao, M. Shafiq, G. Srivastava, A. R. Javed, T. R. Gadekallu, and S. Yin, (2023) “FLPK-BiSeNet: Federated learning based on priori knowledge and bilateral segmentation network for image edge extraction" IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 20(2): 1529–1542. DOI: 10.1109/TNSM.2023.3273991.
- [26] S. Jang, H. Lee, W. J. Kim, J. Lee, S. Woo, and S. Lee, (2024) “Multi-scale structural graph convolutional net work for skeleton-based action recognition" IEEE Trans actions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 34(8): 7244–7258. DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3375512.
- [27] E. Dastbaravardeh, S. Askarpour, M. Saberi Anari, and K. Rezaee, (2024) “Channel attention-based approach with autoencoder network for human action recognition in low-resolution frames" International Journal of Intelligent Systems 2024(1): 1052344. DOI: 10.1155/2024/1052344.
- [28] H. Xu, Y. Gao, Z. Hui, J. Li, and X. Gao, (2025) “Language knowledge-assisted representation learning for skeleton-based action recognition" IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 27: 5784–5799. DOI: 10.1109/TMM. 2025.3543034.
- [29] S.B.Khobdeh,M.R.Yamaghani,andS.K.Sareshkeh, (2024) “Basketball action recognition based on the com bination of YOLO and a deep fuzzy LSTM network: SB Khobdeh et al." The Journal of Supercomputing 80(3): 3528–3553. DOI: 10.1007/s11227-023-05611-7.
- [30] A. O. Kolawole, M. E. Irhebhude, and P. O. Odion, (2025) “Human Action Recognition in Military Obstacle Crossing Using HOG and Region-Based Descriptors" Journal of Computing Theories and Applications 2(3): 410–426. DOI: 10.62411/jcta.12195.
- [31] M. A. Khan, K. Javed, S. A. Khan, T. Saba, U. Habib, J. A. Khan, and A. A. Abbasi, (2024) “Human action recognition using fusion of multiview and deep features: an application to video surveillance" Multimedia tools and applications 83(5): 14885–14911. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-020-08806-9.
- [32] A. C. Cob-Parro, C. Losada-Gutiérrez, M. Marrón Romera, A. Gardel-Vicente, and I. Bravo-Munoz, (2024) “A new framework for deep learning video based Human Action Recognition on the edge" Expert Systems with Applications 238: 122220. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa. 2023.122220.
- [33] X. Wang, S. Zhang, J. Cen, C. Gao, Y. Zhang, D. Zhao, and N. Sang, (2024) “Clip-guided prototype modulating for few-shot action recognition" International Journal of Computer Vision 132(6): 1899–1912. DOI: 10.1007/s11263-023-01917-4.