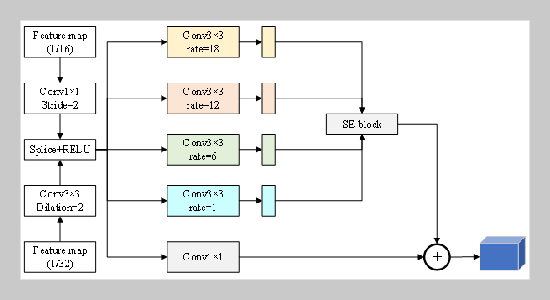
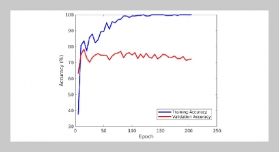
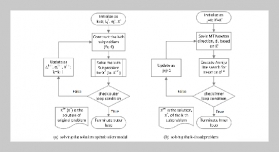
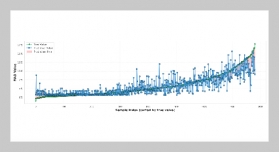
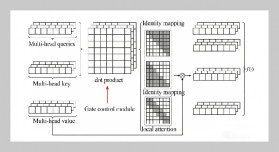
- [1] H.Meng,X. Hong, C. Wang, M. Shang, and W. Zuo, (2024) “Multi-modal crowd counting via a broker modal ity": 231–250. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-72904-1_14.
- [2] L. Deng, Q. Zhou, S. Wang, J. M. Górriz, and Y. Zhang, (2024) “Deep learning in crowd counting: A sur vey" CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology 9(5): 1043–1077. DOI: 10.1049/cit2.12241.
- [3] W. Wang, Q. Liu, and W. Wang, (2022) “Pyramid dilated deep convolutional neural network for crowd counting" Applied Intelligence 52(2): 1825–1837. DOI: 10.1007/s10489-021-02537-6.
- [4] M.-h. Oh, P. Olsen, and K. N. Ramamurthy. “Crowd counting with decomposed uncertainty”. In: Proceed ings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 34. 07. 2020, 11799–11806. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6852.
- [5] S. Yin, L. Wang, T. Chen, H. Huang, J. Gao, J. Zhang, M. Liu, P. Li, and C. Xu, (2025) “LKAFormer: A Lightweight Kolmogorov-Arnold Transformer Model for Image Semantic Segmentation" ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology: DOI: 10.1145/3759254.
- [6] Y. Li, X. Zhang, and D. Chen. “Csrnet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018, 1091–1100. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00120.
- [7] W. Liu, M. Salzmann, and P. Fua. “Context-aware crowd counting”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2019, 5099–5108. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00524.
- [8] Y. Meng, H. Zhang, Y. Zhao, X. Yang, X. Qian, X. Huang, and Y. Zheng. “Spatial uncertainty-aware semi-supervised crowd counting”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vi sion. 2021, 15549–15559. DOI: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01526.
- [9] M. Wang, H. Cai, X.-F. Han, J. Zhou, and M. Gong, (2022) “STNet: Scale tree network with multi-level auxiliator for crowd counting" IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 25: 2074–2084. DOI: 10.1109/TMM.2022.3142398.
- [10] S. Yin, H. Li, A. A. Laghari, L. Teng, T. R. Gadekallu, and A. Almadhor, (2024) “FLSN-MVO: edge computing and privacy protection based on federated learning Siamese network with multi-verse optimization algorithm for industry 5.0" IEEE Open Journal of the Communi cations Society 6: 3443–3458. DOI: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2024.3520562.
- [11] H. Lin, Z. Ma, X. Hong, Q. Shangguan, and D. Meng. “Gramformer: Learning crowd counting via graph modulated transformer”. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 38. 4. 2024, 3395 3403. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v38i4.28126.
- [12] D. B. Sam and R. V. Babu. “Top-down feedback for crowd counting convolutional neural network”. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelli gence. 32. 1. 2018. DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.12290.
- [13] J. Gao, Q. Wang, and X. Li, (2019) “Pcc net: Perspective crowd counting via spatial convolutional network" IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 30(10): 3486–3498. DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2919139.
- [14] X. Ma, S. Du, and Y. Liu. “A lightweight neural net work for crowd analysis of images with congested scenes”. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE. 2019, 979–983. DOI: 10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803062.
- [15] L. Liang, H. Zhao, F. Zhou, M. Ma, F. Yao, and X. Ji, (2023) “PDDNet: lightweight congested crowd counting via pyramid depth-wise dilated convolution" Applied Intelligence 53(9): 10472–10484. DOI: 10.1007/s10489-022-03967-6.
- [16] J. Yi, Z. Shen, F. Chen, Y. Zhao, S. Xiao, and W. Zhou, (2023) “A lightweight multiscale feature fusion network for remote sensing object counting" IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 61: 1–13. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3238185.
- [17] S. Yin, L. Wang, and L. Teng, (2024) “Threshold seg mentation based on information fusion for object shadow detection in remote sensing images" Computer Science and Information Systems 21(4): 1221–1241. DOI: 10.2298/CSIS231230023Y.
- [18] A. Kumar, S. P. Yadav, and A. Kumar, (2025) “An improved feature extraction algorithm for robust Swin Transformer model in high-dimensional medical image analysis" Computers in biology and medicine 188: 109822. DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109822.
- [19] Z. Ma, X. Wu, A. Chu,L. Huang, and Z. Wei, (2024) “SwinFG:Afine-grainedrecognition scheme based on swintransformer" Expert Systems with Applications 244: 123021. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.123021.
- [20] S. Yin, H. Li, A. A. Laghari, T. R. Gadekallu, G. A. Sampedro, and A. Almadhor, (2024) “An anomaly detection model based on deep auto-encoder and capsule graph convolution via sparrow search algorithm in 6G In ternet of Everything" IEEE Internet of Things Journal 11(18): 29402–29411. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3353337.
- [21] M. A. Kizrak and B. Bolat, (2021) “Crowd density estimation by using attention based capsule network and multi-column CNN" IEEE Access 9: 75435–75445. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081529.
- [22] J. Sang, W. Wu, H. Luo, H. Xiang, and X. Xia, (2019) “Improved Crowd Counting Method Based on Scale-Adaptive Convolutional Neural Network" IEEE Access 7(99): 24411–24419. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS. 2019.2899939.
- [23] Z. Chen, S. Zhang, X. Zheng, X. Zhao, and Y. Kong, (2023) “Crowd counting based on multiscale spatial guided perception aggregation network" IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems: DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3304348.
- [24] J.-a. Cheng, Q. Li, A. Souri, X. Lei, C. Zhang, and M. Gao, (2025) “Towards trustworthy crowd counting by distillation hierarchical mixture of experts for edge based cluster computing" Cluster computing 28(7): 1 15. DOI: 10.1007/s10586-025-05226-y.
- [25] K.-H. Kim, T.-K. Ahn, and S. Kim, (2025) “Estimating Invisible Passenger Count Using CCTV Footage: An Approach Combining Object Detection Models and Machine Learning" IEEE Access: DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3597708.
- [26] Z. Niu, H. Pi, G. Xiao, S. Yang, Z. Tang, and D. Liu, (2025) “Low-Light Domain Enhancement and Multi Domain Progressive Fusion for RGB-T Day-Night Crowd Counting" IEEE Internet of Things Journal: DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3594227.