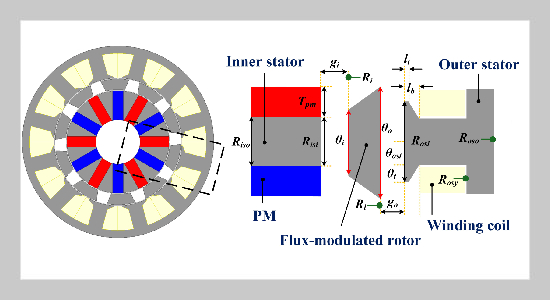
- [1] C. Zhao, M. Cheng, Y. Wang, S. De, S. Shi, C. Song, and Z. Wang, (2024) “Analytical Method of Stator Modal Analysis for Stator-Permanent Magnet Machines" IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 11(1): 2088–2096. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2024.3416187.
- [2] H. Chen, A. M. El-Refaie, and N. A. Demerdash, (2019) “Flux-switching permanent magnet machines: A review of opportunities and challenges—Part I: Fundamentals and topologies" IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 35(2): 684–698. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2019.2956600.
- [3] H. Chen, A. M. EL-Refaie, and N. A. Demerdash, (2019) “Flux-switching permanent magnet machines: A review of opportunities and challenges-part II: Design aspects, control, and emerging trends" IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 35(2): 699–713. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2019.2956565.
- [4] V. I. Vlachou, G. K. Sakkas, F. P. Xintaropoulos, M. S. C. Pechlivanidou, T. D. Kefalas, M. A. Tsili, and A. G. Kladas, (2024) “Overview on permanent magnet motor trends and developments" Energies 17(2): 538. doi: 10.3390/en17020538.
- [5] D. Wu, J. T. Shi, Z. Zhu, and X. Liu, (2014) “Electromagnetic performance of novel synchronous machines with permanent magnets in stator yoke" IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 50(9): 1–9. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2014.2317794.
- [6] S. Cai, J. L. Kirtley, and C. H. Lee, (2022) “Critical review of direct-drive electrical machine systems for electric and hybrid electric vehicles" IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 37(4): 2657–2668. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2022.3197351.
- [7] Z. Wu, Z. Zhu, and J. Shi, (2015) “Novel doubly salient permanent magnet machines with partitioned stator and iron pieces rotor" IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 51(5): 1–12. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2015.2404826.
- [8] Z. Q. Zhu,(2018) “Overview of novel magnetically geared machines with partitioned stators" IET Electric Power Applications 12(5): 595–604. doi: 10.1049/iet-epa.2017.0680.
- [9] H. Yang, H. Zheng, Z. Zhu, H. Lin, S. Lyu, and Z. Pan, (2019) “Comparative study of partitioned stator memory machines with series and parallel hybrid PM configurations" IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 55(7): 1–8. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2019.2894833.
- [10] Y. Du, Y. Mao, F. Xiao, X. Zhu, L. Quan, and F. Li, (2021) “Partitioned stator hybrid excited machine with DC-biased sinusoidal current" IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 69(1): 236–248. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3053901.
- [11] Z. Zhu, H. Hua, D. Wu, J. Shi, and Z. Wu, (2015) “Comparative study of partitioned stator machines with different PMexcitation stators" IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 52(1): 199–208. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2015.2477055.
- [12] L. Wu, G. Ming, L. Zhang, and Y. Fang, (2020) “Improved stator/rotor-pole number combinations for torque ripple reduction in doubly salient PM machines" IEEE Trans actions on Industrial Electronics 68(11): 10601–10611. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3032926.
- [13] C.-S. Lee and H.-J. Kim, (2022) “Harmonic order analysis of cogging torque for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor considering manufacturing disturbances" Energies 15(7): 2428. doi: 10.3390/en15072428.
- [14] X. Zhu, W. Hua, and G. Zhang, (2019) “Analysis and re duction of cogging torque for flux-switching permanent magnet machines" IEEE Transactions on Industry Ap plications 55(6): 5854–5864. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2019.2938721.
- [15] J. Chen, J. Yang, W. Liu, G. Yang, and C. Zhang, (2025) “Effect of Flux Density Harmonics on Torque Characteristics of Integer Slot and Fractional Slot PMSMs" IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion: doi: 10.1109/TEC.2025.3525504.
- [16] L. Jing, W. Tang, W. Liu, Y. Rao, C. Tan, and R. Qu, (2022) “A double-stator single-rotor magnetic field modulated motor with HTS bulks" IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity 32(6): 1–5. doi: 10.1109/TASC.2022.3153242.
- [17] Z. Ding, C. He, C. Feng, and J. Yang, (2022) “A new dual stator permanent magnet machine based on field modulation theory" Sustainability 15(1): 281. doi: 10.3390/su15010281.
- [18] D. Brodnevs and A. Serebrjakovs. “Influence of the rotor tooth longitudinal section shape on the characteristics of inductor alternator”. In: 2022 IEEE 63th International Scientific Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering of Riga Technical University (RTUCON). IEEE. 2022, 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RTUCON56726.2022.9978836.
- [19] H. Sun and K. Wang, (2018) “Effect of third harmonic f lux density on cogging torque in surface-mounted permanent magnet machines" IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 66(8): 6150–6158. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2875639.
- [20] M. Kimiabeigi, J. D. Widmer, R. Long, Y. Gao, J. Goss, R. Martin, T. Lisle, J. S. Vizan, A. Michaelides, and B. Mecrow, (2015) “High-performance low-cost electric motor for electric vehicles using ferrite magnets" IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 63(1): 113–122. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2472517.
- [21] L. Wang, S. Lu, and Y. Chen, (2023) “Two-dimensional analytical models for cogging torque prediction in interior permanent magnet machine" Machines 11(2): 233. doi: 10.3390/machines11020233.
- [22] M. Zhu, L. Wu, D. Liu, Y. Shen, R. Li, and H. Wen, (2025) “Comparative Study of Dual-Stator Permanent Magnet Ma chines with Different PM Arrangements and Rotor Topologies for Aviation Electric Propulsion" Machines 13(4): 273. doi: 10.3390/machines13040273.
- [23] C. Sikder, I. Husain, and W. Ouyang, (2015) “Cogging torque reduction in flux-switching permanent-magnet ma chines by rotor pole shaping" IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 51(5): 3609–3619. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2015.2416238.
- [24] H. Li, M. Feng, L. Lei, Y. Geng, and J. Wang, (2024) “Re search on Cogging Torque Reduction of Direct-Drive Type Dual-Rotor Radial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Propulsion Aircraft" Energies 17(7): 1583. doi: 10.3390/en17071583.
- [25] A. Siritaratiwat, P. Seangwong, A. Butkaew, P. Khunkitti, and W.Sriwannarat, (2025) “In-depth analysis of magnetic f lux concentration indicator in novel curved slots of multi tooth dual-PM doubly salient machine" Scientific Reports 15(1): 13928. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99299-9.
- [26] X. Zhu, C. H. Lee, C. Chan, L. Xu, and W. Zhao, (2020) “Overview of flux-modulation machines based on flux modulation principle: Topology, theory, and development prospects" IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 6(2): 612–624. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2020.2981899.
- [27] Z. Xiang, Y. Zhou, X. Zhu, L. Quan, D. Fan, and Q. Liu, (2023) “Research on characteristic airgap harmonics of a double-rotor flux-modulated PM motor based on harmonic dimensionality reduction" IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 10(3): 5750–5761. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2023.3318648.
- [28] L. Wu, G. Ming, L. Zhang, Y. Fang, T. Li, and W. Zheng, (2021) “Comparative study between doubly salient PM machine with new stator/rotor-pole number combination and biased flux PM machine" IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 57(3): 2354–2365. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2021.3058200.
- [29] H. Kim, Y. Han, K. Lee, and S. Bhattacharya, (2020) “A sinusoidal current control strategy based on harmonic voltage injection for harmonic loss reduction of PMSMs with non-sinusoidal back-EMF" IEEE transactions on industry applications 56(6): 7032–7043. doi: 10.1109/ TIA.2020.3016210.
- [30] E. Kontodinas, P. Karamanakos, A. Kraemer, and S. Wen del. “Optimized pulse patterns for synchronous machines with non-sinusoidal back-EMF”. In: 2023 25th Euro pean Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’23 ECCE Europe). IEEE. 2023, 1–9. doi: 10.23919/ EPE23ECCEEurope58414.2023.10264646.
- [31] Y. Cui, M. Faizan, and Z. Chen, (2021) “Back EMF wave form comparison and analysis of two kinds of electrical machines" World Electric Vehicle Journal 12(3): 149. doi: 10.3390/wevj12030149.
- [32] Y. Du, J. Zhao, F. Xiao, X. Zhu, L. Quan, and F. Li, (2021) “Partitioned stator hybrid excitation doubly salient machine with slot Halbach PM arrays" IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 70(4): 3187–3196. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3065670.
- [33] G. Ming, J. Yuan, S. Ma, J. Yang, L. Si, and W. Shen. “Performance Comparison of Stator Partitioned Doubly Salient Permanent Magnet Motors with Diverse Number of Permanent Magnets”. In: 2022 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific). IEEE. 2022, 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ITECAsia-Pacific56316.2022.9941909.
- [34] N. G. Ozcelik, U. E. Dogru, M. Imeryuz, and L. T. Ergene, (2019) “Synchronous reluctance motor vs. induction motor at low-power industrial applications: Design and comparison" Energies 12(11): 2190. doi: 10.3390/en12112190.
- [35] M. U. Naseer, A. Kallaste, B. Asad, T. Vaimann, and A. Rassõlkin, (2021) “A review on additive manufacturing possibilities for electrical machines" Energies 14(7): 1940. doi: 10.3390/en14071940.
- [36] S. A. A. S. Bukhari and V. Kumar, (2024) “Development of a Synchronous Reluctance Motor for Industrial application" Sukkur IBA Journal of Emerging Technologies 7(1): 15–23. doi: 10.30537/sjet.v7i1.1461.
- [37] G. Chen, J. Xia, J. H. Park, H. Shen, and G. Zhuang, (2021) “Robust sampled-data control for switched com plex dynamical networks with actuators saturation" IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 52(10): 10909–10923. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3069813.
- [38] G. Chen, G. Du, J. Xia, X. Xie, and J. H. Park, (2023) “Controller synthesis of aperiodic sampled-data networked control system with application to interleaved flyback mod ule integrated converter" IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers 70(11): 4570–4580. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2023.3295940.