Shi-Hung Hoang1 , Gor-Don Horng1 , Chen-Yu Chiang1 , Cheng-Hao Ko This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Yi-Chung Lo2 , Ching-Iue Chen2 and Chao-Kang Chang3 1Graduate School of Electro-Optical Engineering Yuan Ze University Chungli, Taiwan 320, R.O.C.
2National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center Hsinchu, Taiwan 300, R.O.C.
3Union Chemical Laboratories Industrial Technology Research Institute Hsinch, Taiwan 300, R.O.C.
Received:
February 11, 2004
Accepted:
February 25, 2004
Publication Date:
June 1, 2004
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2004.7.2.09
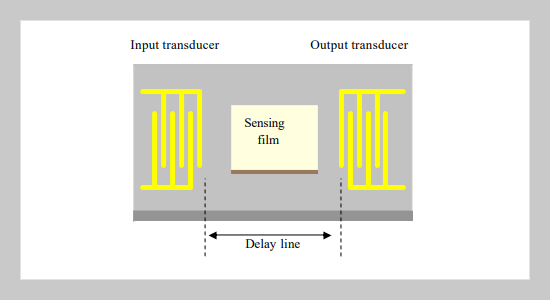
In this paper, we propose a novel characterization technique of the SAW chemical sensors. It combines the technique of electronic frequency shifting measurement (phase lock lop) with the IR microscopic spectral analyzer and performs a in-situ measurement. Using this method, we could conduct ultrahigh sensitive measurement in mass change (a few ppb-a few ppm range) of the SAW chemical sensors by cross-compared with the electronic signals of the SAW device and the FT-IR spectro-microscopic data of the molecular imprinted polymer (MIP) recognition thin film which deposit on the surface of the SAW device. With the use of the MIP thin films, we are able to provide a more accurate molecular selectivity than those current SAW chemical sensors which were based on regular chemical absorb films. Spectrum results of MIP films will be presented below.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
SAW, MIP, FT-IR
REFERENCES