REFERENCES
- [1] Andrews, J. G., S. Buzzi, W. Choi, S. V. Hanly, A. Lozano, C. K. Soong, and J. C. Zhang (2014) What will 5G be? IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 32(6), 1065�1081. doi: 10.1109/JSAC. 2014.2328098
- [2] I, C. L., C. Rowell, S. Han, Z. Xu, G. Li, and Z. Pan (2014) Toward green and soft: a 5G perspective, IEEE Communications Magazine 52(2), 66�73. doi: 10. 1109/MCOM.2014.6736745
- [3] Lu, L., Y. Li, A. Lee, A. Ashikhmin, and R. Zhang (2014) An overview of massive MIMO: benefits and challenges, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 8(5), 742�758. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2014. 2317671
- [4] Fernandes, F., A. Ashikhmin, and T. L. Marzetta (2013) Inter-cell interference in non cooperative TDD large scale antenna systems, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 31(2), 1�10.
- [5] Rusek, F., D. Persson, B. K. Lau, E. G. Larsson, T. L. Marzetta, O. Edfors, and F. Tufvesson (2013) Scaling up MIMO: opportunities and challenges with very large arrays, IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30(1), 40�60. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2011.2178495
- [6] Chen, Y., S. Zhang, S. Xu, and G. Y. Li (2011) Fundamental tradeoffs on green wireless networks, IEEE Commun. Mag. 49(6), 30–37. doi: 10.1109/MCOM. 2011.5783982
- [7] Marzetta, T. L. (2010) Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 9(11), 3590–3600. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2010.092810.091092
- [8] Wu, W. C., and C. Y. Hsu (2017) Subcarriers-and-bits allocation algorithms for downlink OFDMA-based MIMO systems, Journal of the Franklin Institute 354(11), 4615–4636. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.04. 019
- [9] Svedman, P., S. K. Wilson, L. J. Cimini, and B. Ottersten (2007) Opportunistic beamforming and scheduling for OFDMA systems, IEEE Trans. on Communications 55(5), 941�952.
- [10] Zhang, Y. J., and K. B. Letaief (2004) Multiuser adaptive subcarrier-and-bit allocation with adaptive cell selection for OFDM systems, IEEE Trans. Wireless Communications 3(5), 1566�1575. doi: 10.1109/TWC. 2004.833501 \
- [11] Ashikhmin, A., and T. L. Marzetta (2012) Pilot contamination precoding in multi-cell large scale antenna systems, 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1137–1141. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2012.6283031
- [12] Jose, J., A. Ashikhmin, T. L. Marzetta, and S. Vishwanath (2011) Pilot contamination and precoding in multi-cell TDD systems, IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 10(8), 2640–2651. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011. 060711.101155
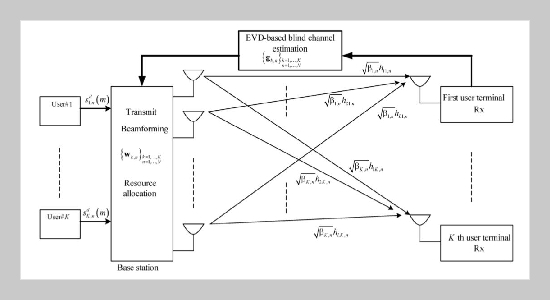
- [13] Ngo, H. Q., and E. G. Larsson (2012) EVD-based channel estimations for multicell multiuser MIMO with very large antenna arrays, Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speed and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan. doi: 10.1109/ ICASSP.2012.6288608
- [14] Xu, F., Y. Xiao, and D. Wang (2014) Adaptive semiblind channel estimation for massive MIMO system, 2014 12th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), 19�23.
- [15] Mawatwal, K., D. Sen, and R. Roy (2017) A semiblind channel estimation algorithm for massive MIMO systems,IEEE Wireless Commun. Letters 6(1), 70�73. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2016.2631535
- [16] Nayebi, E., and B. D. Rao (2018) Semi-blind channel estimation for multiuser massive MIMO systems, IEEE Trans. on Signal Process. 66(2), 540�553. doi: 10. 1109/TSP.2017.2771725
- [17] Lozano, A., A. M. Tulino, and S. Verdú (2008) Optimum power allocation for multiuser OFDM with arbitrary signal constellations, IEEE Trans. on Communications 56(5), 828�837. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2008. 060211
- [18] Wong, I. C., Z. Shen, B. L. Evans, and J. G. Andrews (2004) A low complexity algorithm for proportional resource allocation in OFDMA systems, 2004 IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SIPS). doi: 10.1109/SIPS.2004.1363015
- [19] Jang, J., and K. B. Lee (2003) Transmit power adaptation for multiuser OFDM systems, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 21(2), 828�837. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2002.807348
- [20] Haykin, S. (2001) Communication Systems, Chap. 6, 4th editions, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- [21] Meshkati, F., H. V. Poor, S. C. Schwart, and N. B. Mandayam (2005) An energy-efficient approach to power control and receiver design in wireless data networks, IEEE Trans. on Communications 53(11), 1885� 1894. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2005.858695