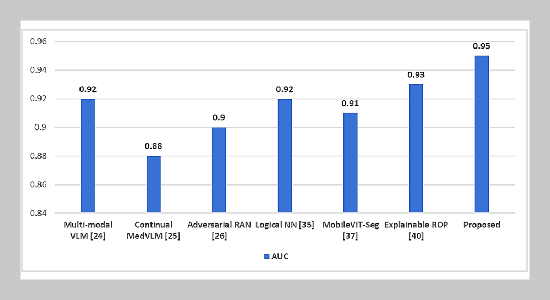
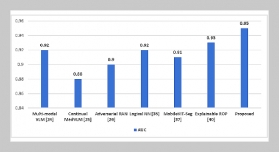
- [1] S. Wang, J. Liu, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Li, H. Wang, X. Luo, S. Liu, L. Liu, and J. Zhang, (2024) “Global, Regional and National Burden of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Childhood and Adolescence: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019" BMJ Paediatrics Open 8(1): e002267. DOI: 10.1136/bmjpo-2023-002267.
- [2] R.-H. Zhang, Y.-M. Liu, L. Dong, H.-Y. Li, Y.-F. Li, W.-D. Zhou, H.-T. Wu, Y.-X. Wang, and W.-B. Wei, (2022) “Prevalence, Years Lived With Disability, and Time Trends for 16 Causes of Blindness and Vision Impairment: Findings Highlight Retinopathy of Prematurity" Fron tiers in Pediatrics 10: DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.735335.
- [3] J. Wang, J. Ji, M. Zhang, J.-W. Lin, G. Zhang, W. Gong, L.-P. Cen, Y. Lu, X. Huang, D. Huang, T. Li, T. K. Ng, and C. P. Pang, (2021) “Automated Explainable Multidimensional Deep Learning Platform of Retinal Images for Retinopathy of Prematurity Screening" JAMA Network Open4(5): e218758. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.8758.
- [4] A. Nair, R. El Ballushi, B. Z. Anklesaria, M. Kamali, M. Talat, and T. Watts, (2022) “A Review on the Incidence and Related Risk Factors of Retinopathy of Prematurity Across Various Countries" Cureus: DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32007.
- [5] Q. Wu, Y. Hu, Z. Mo, R. Wu, X. Zhang, Y. Yang, B. Liu, Y. Xiao, X. Zeng, Z. Lin, Y. Fang, Y. Wang, X. Lu, Y. Song, W. W. Y. Ng, S. Feng, and H. Yu, (2022) “Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Model to Predict the Occurrence and Severity of Retinopathy of Prematurity" JAMA Network Open 5(6): e2217447. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.17447.
- [6] J. Y. Tang, M. P. Marinkovich, E. Lucas, E. Gorell, A. Chiou, Y. Lu, J. Gillon, D. Patel, and D. Rudin, (2021) “A Systematic Literature Review of the Disease Burden in Patients with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa" Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 16(1): 175. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-021-01811-7.
- [7] M. Zhang, C. Qin, and F. Qiang, (2024) “Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Assess Physicians’ Willingness to Share Electronic Medical Records in a Hierarchical Diagnostic Ecosystem" Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 1(1): 27–35. DOI: 10.70891/JAIR.2024.100024.
- [8] Z. A. Shaikh, A. A. Khan, L. Teng, A. A. Wagan, and A. A. Laghari, (2022) “BIoMT Modular Infrastructure: The Recent Challenges, Issues, and Limitations in Blockchain Hyperledger-Enabled E-Healthcare Application" Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2022(1): 3813841. DOI: 10.1155/2022/3813841.
- [9] A. Bai, C. Carty, and S. Dai, (2022) “Performance of Deep-Learning Artificial Intelligence Algorithms in Detecting Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Systematic Re view" Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology 36(3): 296. DOI: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_219_21.
- [10] J. Zhang, Y. Liu, T. Mitsuhashi, and T. Matsuo, (2021) “Accuracy of Deep Learning Algorithms for the Diagnosis of Retinopathy of Prematurity by Fundus Images: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Ophthalmology 2021(1): 8883946. DOI: 10.1155/2021/ 8883946.
- [11] L. F. Nakayama, W. G. Mitchell, L. Z. Ribeiro, R. G. Dychiao, W. Phanphruk, L. A. Celi, K. Kalua, A. P. D. Santiago, C. V. S. Regatieri, and N. S. B. Moraes, (2023) “Fairness and Generalisability in Deep Learning of Retinopathy of Prematurity Screening Algorithms: A Literature Review" BMJ Open Ophthalmology 8(1): DOI: 10.1136/bmjophth-2022-001216.
- [12] P.Rashidian,S.Karami,andS.A.Salehi,(2025)“ARe view on Retinopathy of Prematurity" Medical Hypothesis, Discovery and Innovation in Ophthalmology 13(4): 201–212. DOI: 10.51329/mehdiophthal1511.
- [13] Z. Qin, H. Yi, Q. Lao, and K. Li, (2022) “Medical image understanding with pretrained vision language models: A comprehensive study" arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.15517:
- [14] M. Hu, J. Qian, S. Pan, Y. Li, R. L. Qiu, and X. Yang, (2024) “Advancing medical imaging with language models: featuring a spotlight on ChatGPT" Physics in Medicine & Biology 69(10): 10TR01. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad387d.
- [15] Y. Bazi, M. M. A. Rahhal, L. Bashmal, and M. Zuair, (2023) “Vision–Language Model for Visual Question Answering in Medical Imagery" Bioengineering 10(3): 380. DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10030380.
- [16] P. Chambon, C. Bluethgen, C. P. Langlotz, and A. Chaudhari, (2022) “Adapting Pretrained Vision Language Foundational Models to Medical Imaging Domains" arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04133 (arXiv:2210.04133): DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2210.04133.
- [17] A. Lozano, M. W. Sun, J. Burgess, L. Chen, J. J. Nirschl, J. Gu, I. Lopez, J. Aklilu, A. Rau, A. W. Katzer, et al. “BIOMEDICA: An Open Biomedi cal Image-Caption Archive, Dataset, and Vision Language Models Derived from Scientific Litera ture”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2025, 19724 19735.
- [18] K. Poudel, M. Dhakal, P. Bhandari, R. Adhikari, S. Thapaliya, and B. Khanal, (2023) “Exploring transfer learning in medical image segmentation using vision language models" arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07706 (arXiv:2308.07706): DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2308.07706.
- [19] V. Nath, W. Li, D. Yang, A. Myronenko, M. Zheng, Y. Lu, Z. Liu, H. Yin, Y. M. Law, Y. Tang, et al. “VILA M3: Enhancing Vision-Language Models with Med ical Expert Knowledge”. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference. 2025, 14788–14798.
- [20] S. Yin, H. Li, L. Teng, A. A. Laghari, A. Almadhor, M. Gregus, and G. A. Sampedro, (2024) “Brain CT Image Classification Based on Mask RCNN and Attention Mechanism" Scientific Reports 14(1): 29300. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78566-1.
- [21] T. Shahzad, M. Saleem, M. S. Farooq, S. Abbas, M. A. Khan, and K. Ouahada, (2024) “Developing a Trans parent Diagnosis Model for Diabetic Retinopathy Using Explainable AI" IEEE Access 12: 149700–149709. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3475550.
- [22] S. Abbas, A. Qaisar, M. S. Farooq, M. Saleem, M. Ahmad, and M.A.Khan, (2024) “Smart Vision Transparency: Efficient Ocular Disease Prediction Model Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence" Sensors 24(20): 6618. DOI: 10.3390/s24206618.
- [23] N. Sureja, V. Parikh, A. Rathod, P. Patel, H. Patel, andH.Sureja, (2025) “Explainable Artificial Intelligence Based Deep Learning for Retinal Disease Detection" Journal of Electronics, Electromedical Engineering, and Medical Informatics 7(2): 471–483. DOI: 10.35882/jeeemi.v7i2.717.
- [24] N. Afreen and R. Aluvalu, (2024) “Glaucoma Detection Using Explainable AI and Deep Learning." EAI Endorsed Transactions on Pervasive Health & Technology 10(1): DOI: 10.4108/eetpht.10.5658.
- [25] M.S. Ali and M.Islam, (2023) “A hyper-tuned Vision Transformer model with Explainable AI for Eye disease detection and classification from medical images" BS the sis, Faculty of Engineering and Technology Islamic University:
- [26] Y. Zhong, R. Jin, X. Li, and Q. Dou, (2025) “Can Common VLMsRival Medical VLMs? Evaluation and Strategic Insights" arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.17337: DOI: https: //doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2506.17337.
- [27] J. Chen, D. Yang, Y. Jiang, M. Li, J. Wei, X. Hou, and L. Zhang, (2024) “Efficiency in focus: Layernorm as a catalyst for fine-tuning medical visual language pre trained models" arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.16385: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2404.16385.
- [28] M. Mistretta and A. D. Bagdanov, (2024) “Re-tune: Incremental fine tuning of biomedical vision-language models for multi-label chest x-ray classification" arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.17827: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2410.17827.
- [29] X. Han, L. Jin, X. Ma, and X. Liu, (2024) “Light-weight fine-tuning method for defending adversarial noise in pre trained medical vision-language models" arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.02716: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2407.02716.
- [30] J. Pan, C. Liu, J. Wu, F. Liu, J. Zhu, H. B. Li, C. Chen, C. Ouyang, and D. Rueckert. “MedVLM-R1: Incen tivizing Medical Reasoning Capability of Vision Language Models (VLMs) via Reinforcement Learn ing”. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention– MICCAI 2025. 2025, 337–347. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-032-04981-0_32.
- [31] A. Farrag, G. Gad, Z. M. Fadlullah, M. M. Fouda, and M. Alsabaan, (2023) “An Explainable AI System for Medical Image Segmentation With Preserved Local Resolution: Mammogram Tumor Segmentation" IEEE Access 11: 125543–125561. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3330465.
- [32] A. S. Farhan, M. Khalid, and U. Manzoor, (2025) “XAI-MRI: AnEnsembleDual-Modality Approach for 3D Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence 8: DOI: 10.3389/frai.2025.1525240.
- [33] R. Gipiškis, (2024) “XAI-driven Model Improvements in Interpretable Image Segmentation" xAI-2024 Late breaking work, demos and doctoral consortium joint proceedings, Valletta, Malta, July 17-19, 2024. 369–376.
- [34] N. Sritharan, N. Gnanavel, P. Inparaj, D. Meedeniya, and P. Yogarajah, (2025) “Explainable Artificial Intelligence Driven Segmentation for Cervical Cancer Screening" IEEE Access 13: 71306–71322. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3561178.
- [35] P. K. Rao, S. Chatterjee, M. Janardhan, K. Nagaraju, S. B. Khan, A. Almusharraf, and A. I. Alharbe, (2023) “Optimizing Inference Distribution for Efficient Kidney Tumor Segmentation Using a UNet-PWP Deep-Learning Model with XAI on CT Scan Images" Diagnostics 13(20): 3244. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13203244.
- [36] F. Motzkus, (2023) “xAI-based Model Improvement for Detection and Image Segmentation": DOI: 10.18420/KI2023-DC-08.
- [37] M.H.Alikhani, (2025) “Synthetic reasoning-Designing AI Architectures Beyond Neural Networks with Hybrid Neuro-Symbolic Systems" Available at SSRN 5226493: DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.5226493.
- [38] Q. Lu, R. Li, E. Sagheb, A. Wen, J. Wang, L. Wang, J. W. Fan, and H. Liu, (2025) “Explainable Diagnosis Prediction through Neuro-Symbolic Integration" AMIA Summits on Translational Science Proceedings 2025: 332–341. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3529133.
- [39] Y. Chudasama, H. Huang, D. Purohit, and M.-E. Vi dal, (2025) “Towards interpretable hybrid ai: Integrating knowledge graphs and symbolic reasoning in medicine" IEEE Access 13: 39489–39509. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS. 2025.3529133.
- [40] S. Bangalore Vijayakumar, K. T. Chitty-Venkata, K. Arya, and A. K. Somani, (2024) “Convision benchmark: A contemporary framework to benchmark cnn and vit models" AI 5(3): 1132–1171. DOI: 10.3390/ai5030056.
- [41] Y. Yang, L. Zhang, L. Ren, and X. Wang, (2023) “MMViT-Seg: A Lightweight Transformer and CNN Fusion Network for OVID-19 Segmentation" Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 230: 107348. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107348.
- [42] H. Wang, X. Dai, S. Ning, J. Ye, G. Srivastava, F. Khan, S. T. U. Shah, and Y. Pan, (2025) “TinyVit-LightGBM: A Lightweight and Smart Feature Fusion Framework for IoMT-based Cancer Diagnosis" Information Fusion 122: 103180. DOI: 10.1016/j.inffus.2025.103180.
- [43] P. Li and J. Liu, (2022) “Early Diagnosis and Quantitative Analysis of Stages in Retinopathy of Prematurity Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks" Translational Vision Science & Technology 11(5): 17. DOI: 10.1167/tvst.11.5.17.
- [44] M.Mehmood,M.Alsharari,S.Iqbal,I.Spence,andM. Fahim. “Retina Lite Net: A Lightweight Transformer Based CNN for Retinal Feature Segmentation”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024, 2454–2463.
- [45] D. R. K. Dhanaraj and A. Kakade, (2024) “Optimized Spatial Automatic Color Enhancement Technique: A Novel Approach for Color Restoration in Retinopathy of Prematurity (Rop) Retinal Images" Available at SSRN 4965374 (4965374): DOI: 10.2139/ssrn.4965374.
- [46] F. Parodi, J. K. Matelsky, A. Regla-Vargas, E. E. Foglia, C. Lim, D. Weinberg, K. P. Kording, H. M. Herrick, and M. L. Platt. “Vision-Language Models for De coding Provider Attention During Neonatal Resus citation”. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2024, 343–353.
- [47] B. C. Kalpelbe, A. G. Adaambiik, and W. Peng, (2025) “Vision Language Models in Medicine" arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.01863 (arXiv:2503.01863): DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.01863.
- [48] R. Wang, Q. Yao, Z. Jiang, H. Lai, Z. He, X. Tao, and S. K. Zhou, (2025) “ECAMP: Entity-centered Context aware Medical Vision Language Pre-training" Medical Image Analysis 105: 103690. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2025.103690.
- [49] J. Ji, Y. Hou, X. Chen, Y. Pan, and Y. Xiang, (2024) “Vision-Language Model for Generating Textual Descriptions From Clinical Images: Model Development and Vali dation Study" JMIR Formative Research 8(1): e32690. DOI: 10.2196/32690.
- [50] R. Ghnemat, S. Alodibat, and Q. Abu Al-Haija, (2023) “Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) for Deep Learning Based Medical Imaging Classification" Journal of Imaging 9(9): 177. DOI: 10.3390/jimaging9090177.
- [51] G. T. Neamah, M. Q. Al Nwuaini, K. A. Abd, A. J. M. Nasrawi, and S. R. M. Hussein, (2022) “Retinopathy of Prematurity, a Two-Year Experience at the ROP Screening Unit from AL-Zahraa Teaching Hospital, AL-Najaf, Iraq" Journal of Medicine and Life 15(11): 1431–1436. DOI: 10.25122/jml-2022-0060.
- [52] M. Dhahir Al-Mendalawi, (2024) “Presentation of Retinopathy of Prematurity and Associated Risk Factor in a Referral Center in Iraq" Arab Board Medical Journal 25(1): 45. DOI: 10.4103/abmj.abmj_38_23.
- [53] M. F. Chiang, G. E. Quinn, A. R. Fielder, and R. Chan, (2022) “International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity, 3rd Edition (ICROP3)" Journal of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (JAAPOS) 26(4): e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2022.08.013.
- [54] A. Bai, S. Dai, J. Hung, A. Kirpalani, H. Russell, J. Elder, S. Shah, C. Carty, and Z. Tan, (2023) “Multi center Validation of Deep Learning Algorithm ROP.AI for the Automated Diagnosis of Plus Disease in ROP" Translational Vision Science & Technology 12(8): 13. DOI: 10.1167/tvst.12.8.13.
- [55] J. L. McKee, M. C. Kaufman, A. K. Gonzalez, M. P. Fitzgerald, S. L. Massey, F. Fung, S. K. Kessler, S. Witzman, N. S. Abend, and I. Helbig, (2023) “Lever aging Electronic Medical Record-Embedded Standardised Electroencephalogram Reporting to Develop Neona tal Seizure Prediction Models: A Retrospective Cohort Study" The Lancet Digital Health 5(4): e217–e226. DOI: 10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00004-3.
- [56] N.Ghanbari,(2025)“EnhancingtheDetail Resolution of Foggy Images Using Fuzzy Histogram Equalization with Weighted Distribution" Current Applied Sciences: 1 14. DOI: 10.22034/cas.2025.520327.1048.
- [57] X. Liu, T. Nguyen, et al., (2024) “Medical Images Enhancement by Integrating CLAHE with Wavelet Trans form and Non-Local Means Denoising" Academic Journal of Computing & Information Science 7(1): DOI: 10.25236/AJCIS.2024.070108.
- [58] W. Tian, X. Huang, T. Cheng, W. He, J. Fang, R. Feng, D. Geng, and X. Zhang, (2025) “A Medical Multimodal Large Language Model for Pediatric Pneumonia" IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 29(9): 6869–6882. DOI: 10.1109/JBHI.2025.3569361.