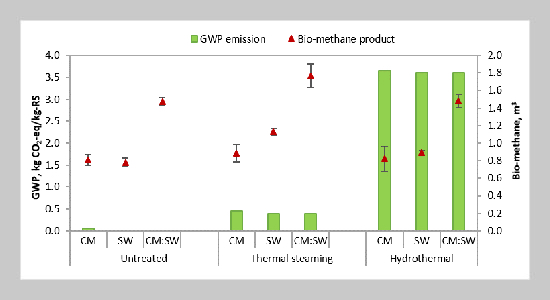
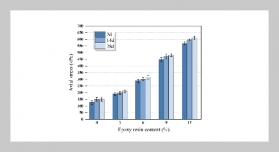
- [1] S. Maneepitak, H. Ullah, K. Paothong, B. Kachen chart, A. Datta, and R. P. Shrestha, (2019) “Effect of water and rice straw management practices on yield and water productivity of irrigated lowland rice in the Central Plain of Thailand" Agricultural Water Management 211: 89–97. DOI: 10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.041.
- [2] W.Attavanich and P. Pengthamkeerati, (2018) “Sup port to the development and implementation of the Thai climate change policy: experts on GHG mitigation options in the Thai agriculture sector" Funded by Deutsche Gesellschaft fü r Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH under the supervision of Office for National Economic Planning (ONEP) & Office of Agricultural Economics (OAE)(Unpublished re port):
- [3] A. Junpen, J. Pansuk, O. Kamnoet, P. Cheewaphong phan, and S. Garivait, (2018) “Emission of Air Pollutants from Rice Residue Open Burning in Thailand, 2018" Atmosphere 9(11): 449. DOI: 10.3390/atmos9110449.
- [4] P.-T. H. Phuong, T.-D. Nghiem, P.-T. M. Thao, C.-T. Pham, T.-T. Thi, and N. T. Dien, (2021) “Impact of rice straw open burning on local air quality in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam" Atmospheric Pollution Research 12(11): 101225. DOI: 10.1016/j.apr.2021.101225.
- [5] G. He, T. Liu, and M. Zhou, (2020) “Straw burning, PM2.5, and death: Evidence from China" Journal of Development Economics 145: 102468. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jdeveco.2020.102468.
- [6] K.LaskoandK.Vadrevu,(2018)“Improvedriceresidue burning emissions estimates: Accounting for practice specific emission factors in air pollution assessments of Vietnam" Environmental Pollution 236: 795–806. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.098.
- [7] W. Wang, D. Y. Lai, J. Sardans, C. Wang, A. Datta, T. Pan, C. Zeng, M. Bartrons, and J. Penuelas, (2015) “Rice straw incorporation affects global warming potential differently in early vs. late cropping seasons in South eastern China" Field Crops Research 181: 42–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.07.007.
- [8] C.Krittanawong, Y. K. Qadeer, R. B. Hayes, Z. Wang, G. D. Thurston, S. Virani, and C. J. Lavie, (2023) “PM2.5 and cardiovascular diseases: State-of-the-Art re view" International Journal of Cardiology: Cardio vascular Risk and Prevention 19: 200217. DOI: 10. 1016/j.ijcrp.2023.200217.
- [9] P. Ramesh, V. A. M. Selvan, and D. Babu, (2022) “Se lection of sustainable lignocellulose biomass for second generation bioethanol production for automobile vehicles using lifecycle indicators through fuzzy hybrid PyMCDM approach" Fuel 322: 124240. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124240.
- [10] N.V. C. Ngan, F. M. S. Chan, T. S. Nam, H. Van Thao, M. C. Maguyon-Detras, D. V. Hung, D. M. Cuong, and N. Van Hung, (2020) “Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw for Biogas Production" Sustainable rice straw management: 65–92. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32373 8_5.
- [11] F.-M. Pellera and E. Gidarakos, (2018) “Chemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic agroindustrial waste for methane production" Waste Management 71: 689–703. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.038.
- [12] H. Carrere, G. Antonopoulou, R. Affes, F. Passos, A. Battimelli, G. Lyberatos, et al., (2016) “Review of feedstock pretreatment strategies for improved anaerobic digestion: From lab-scale research to full-scale application" Bioresource Technology 199: 386–397. DOI: 10.1016/ j.biortech.2015.09.007.
- [13] J. Zhao, X. Ge, J. Vasco-Correa, and Y. Li, (2014) “Fun gal pretreatment of unsterilized yard trimmings for enhanced methane production by solid-state anaerobic di gestion" Bioresource Technology 158: 248–252. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.029.
- [14] H. Chen, J. Liu, X. Chang, D. Chen, Y. Xue, P. Liu, H. Lin, and S. Han, (2017) “A review on the pretreatment of lignocellulose for high-value chemicals" Fuel Processing Technology 160: 196–206. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2016. 12.007.
- [15] M. Ge, Y. Liu, J. Zhou, and M. Jin, (2022) “Densification pretreatment triggers efficient methanogenic performance and robust microbial community during anaerobic digestion of corn stover" Bioresource Technology 362: 127762. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127762.
- [16] M. Shahabazuddin, B. K. Banuvalli, N. Mulik, A. Pande, V. Bokade, and S. N. Mudliar, (2023) “Com parative studies of the influence of particle size on various pretreatments of rice husk by assessment of chemical and structural components and wastewater characteristics of liquid fraction" Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery 13(6): 5243–5252. DOI: 10.1007/s13399-021-01565-z.
- [17] T. Luo, H. Huang, Z. Mei, F. Shen, Y. Ge, G. Hu, and X. Meng, (2019) “Hydrothermal pretreatment of rice straw at relatively lower temperature to improve biogas production via anaerobic digestion" Chinese Chemical Letters 30(6): 1219–1223. DOI: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.03.018.
- [18] B.-l. Dai, X.-j. Guo, D.-h. Yuan, and J.-m. Xu, (2018) “Comparison of Different Pretreatments of Rice Straw Substrate to Improve Biogas Production" Waste and Biomass Valorization 9(9): 1503–1512. DOI: 10.1007/ s12649-017-9950-9.
- [19] J. Zhou, B. Yan, Y. Wang, X. Yong, Z. Yang, H. Jia, M. Jiang, and P. Wei, (2016) “Effect of steam explosion pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of rice straw" RSC Advances 6(91): 88417–88425. DOI: 10.1039/ c6ra15330e.
- [20] M. Dehghani, K. Karimi, andM.Sadeghi, (2015) “Pre treatment of Rice Straw for the Improvement of Biogas Production" Energy & Fuels 29(6): 3770–3775. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00718.
- [21] R. D. Coura, A. Ferraz, and A. C. Rodrigues, (2016) “Co-digestion of cattle manure and sewage sludge: effects on biodegradation rates" International Journal of Advances in Science Engineering and Technology 4(1): 88–91.
- [22] X. Zou, Y. Wang, Y. Dai, S. Zhou, B. Wang, Y. Li, and J. Li, (2022) “Batch and semi-continuous experiments examining the sludge mesophilic anaerobic digestive perfor mance with different varieties of rice straw" Bioresource Technology 346: 126651. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021. 126651.
- [23] H. Zhang, D. An, Y. Cao, Y. Tian, and J. He, (2021) “Modeling the Methane Production Kinetics of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Agricultural Wastes Using Sigmoidal Functions" Energies 14(2): 258. DOI: 10.3390/ en14144212.
- [24] Y. Wang, X. Zhou, B. Dai, and X. Zhu, (2021) “Improvement of anaerobic co-digestion of plant waste and excess sludge using calcium peroxide" Environmental Science and Pollution Research 28(34): 47540–47549. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14055-6.
- [25] N. S. Tran, T. Van Huynh, N. V. C. Nguyen, and K. Ingvorsen, (2021) “Bio-pretreatment Enhances Biogas Production from Co-digestion of Rice Straw and Pig Manure" International Energy Journal 21(4): 457–466.
- [26] L. Wei, K. Qin, J. Ding, M. Xue, C. Yang, J. Jiang, and Q. Zhao, (2019) “Optimization of the co-digestion of sewage sludge, maize straw and cow manure: microbial responses and effect of fractional organic characteristics" Scientific Reports 9(1): 2374. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-38829-8.
- [27] S. M. Hallaji, M. Kuroshkarim, and S. P. Moussavi, (2019) “Enhancing methane production using anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge with combined fruit waste and cheese whey" BMC Biotechnology 19(1): 19. DOI: 10.1186/s12896-019-0513-y.
- [28] F. M. S. Silva, C. F. Mahler, L. B. Oliveira, and J. P. Bassin, (2018) “Hydrogen and methane production in a two-stage anaerobic digestion system by co-digestion of food waste, sewage sludge and glycerol" Waste Management 76: 339–349. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.02.039.
- [29] S. Jijai and C. Siripatana, (2017) “Kinetic Model of Bio gas Production from Co-digestion of Thai Rice Noodle Wastewater (Khanomjeen) with Chicken Manure" En ergy Procedia 138: 386–392. DOI: 10.1016/j.egypro. 2017.10.177.
- [30] F. S. bibinitperiod T. C. Shaikh Mahfuzur Rahman, (2018) “Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Municipal Sewage Sludge with Cow Dung at Different Ratio" Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science 18(3): 14–20. DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.33760.53766.
- [31] J. Ye, D. Li, Y. Sun, G. Wang, Z. Yuan, F. Zhen, and Y. Wang, (2013) “Improved biogas production from rice straw by co-digestion with kitchen waste and pig manure" Waste Management 33(12): 2653–2658. DOI: 10.1016/ j.wasman.2013.05.014.
- [32] S. Areeya, E. J. Panakkal, P. Kunmanee, A. Tawai, S. Amornraksa, M. Sriariyanun, A. Kaoloun, N. Hartini, Y.-S. Cheng, M. Kchaou, et al., (2024) “A Review of Sugarcane Biorefinery: From Waste to Value-Added Prod ucts" Applied Science and Engineering Progress 17(3): 7402. DOI: 10.14416/j.asep.2024.06.004.
- [33] J. Kainthola, M. Shariq, A. S. Kalamdhad, and V. V. Goud, (2021) “Comparative study of different thermal pretreatment techniques for accelerated methane production from rice straw" Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery 11(4): 1145–1154. DOI: 10.1007/s13399-019 00537-8.
- [34] L. You, S. Yu, H. Liu, C. Wang, Z. Zhou, L. Zhang, and D. Hu, (2019) “Effects of biogas slurry fertilization on fruit economic traits and soil nutrients of Camellia oleifera Abel" PLOS ONE 14(5): e0208289. DOI: 10. 1371/journal.pone.0208289.
- [35] M. Xu, Y. Xian, J. Wu, Y. Gu, G. Yang, X. Zhang, H. Peng, X. Yu, Y. Xiao, and L. Li, (2019) “Effect of biogas slurry addition on soil properties, yields, and bacterial composition in the rice-rape rotation ecosystem over 3 years" Journal of Soils and Sediments 19(5): 2534 2542. DOI: 10.1007/s11368-019-02258-x.
- [36] M. Khemkhao, S. Lee, C. Phalakornkule, and V. Dom rongpokkaphan, (2025) “Experimental and kinetic analysis of the addition of zerovalent iron for promoting con version of CO2 into CH4 by anaerobic sludge" Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 28(10): 2043–2049. DOI: 10.6180/jase.202510_28(10).0016.
- [37] R. Baird, A. Eaton, and W. Federation, (2017) “Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewa ter, Item Details" American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC:
- [38] F. A. Aguilar-Aguilar, D. L. Nelson, L. d. A. Pantoja, and A. Santos, (2017) “Study of anaerobic co-digestion of crude glycerol and swine manure for the production of biogas" Revista Virtual de Química 9(6): 2383–2403. DOI: 10.21577/1984-6835.20170142.
- [39] FAMIC, (2020) “Testing Methods For Fertilizers" Incorporated Administrative Agency Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center:
- [40] A. Walkley and I. A. Black, (1934) “An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method" Soil science 37(1): 29–38.
- [41] E. Bolyen, J. R. Rideout, M. R. Dillon, N. A. Bokulich, C. C. Abnet, G. A. Al-Ghalith, H. Alexander, E. J. Alm, M. Arumugam, F. Asnicar, et al., (2019) “Repro ducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2" Nature Biotechnology 37(8): 852–857. DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9.
- [42] K. Dhamodharan, V. Kumar, and A. S. Kalamdhad, (2015) “Effect of different livestock dungs as inoculum on food waste anaerobic digestion and its kinetics" Biore source Technology 180: 237–241.
- [43] R. Beck, (1999) “Soil Analysis Handbook of Reference Methods" Soil and Plant Analysis Council Inc.
- [44] C. Bower and L. Wilcox, (1965) “Soluble salts" Methods of soil analysis: Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties 9: 933–951.
- [45] Q.-L. Wu, W.-Q. Guo, H.-S. Zheng, H.-C. Luo, X.-C. Feng, R.-L. Yin, and N.-Q. Ren, (2016) “Enhancement of volatile fatty acid production by co-fermentation of food waste and excess sludge without pH control: the mecha nism and microbial community analyses" Bioresource Technology 216: 653–660. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech. 2016.06.006.
- [46] J. W. Lim, J. A. Chiam, and J.-Y. Wang, (2014) “Microbial community structure reveals how microaeration improves fermentation during anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste" Bioresource Technology 171: 132–138. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.050.
- [47] T. Tang, J. Li, Z. Yang, X. Luo, and Y. Chen, (2019) “Effect of straw on microbial community composition and degradation efficiency of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sludge digester" International Journal of Environ mental Science and Technology 16(12): 7973–7986. DOI: 10.1007/s13762-019-02261-2.
- [48] A. Hiraishi, M. Iwasaki, and H. Shinjo, (2000) “Terminal restriction pattern analysis of 16S rRNA genes for the characterization of bacterial communities of activated sludge" Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 90(2): 148–156. DOI: 10.1016/S1389-1723(00)80102-4.
- [49] J. Yi, B. Dong, J. Jin, and X. Dai, (2014) “Effect of increasing total solids contents on anaerobic digestion of food waste under mesophilic conditions: performance and microbial characteristics analysis" PLoS ONE 9(7): e102548. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102548.
- [50] R. Tian, D. Ning, Z. He, P. Zhang, S. J. Spencer, S. Gao, W. Shi, L. Wu, Y. Zhang, Y. Yang, et al., (2020) “Small and mighty: adaptation of superphylum Patescibacteria to groundwater environment drives their genome simplicity" Microbiome8(1): 51. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-020-00825 w.
- [51] D. H. Lee, S. K. Behera, J. W. Kim, and H.-S. Park, (2009) “Methane production potential of leachate generated from Korean food waste recycling facilities: a lab scale study" Waste Management 29(2): 876–882. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.06.033.
- [52] D. Cheng, H. Ngo, W. Guo, S. Chang, D. Nguyen, S. M. Kumar, B. Du, Q. Wei, and D. Wei, (2018) “Prob lematic effects of antibiotics on anaerobic treatment of swine wastewater" Bioresource Technology 263: 642 653. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.010.
- [53] J.-L. Garcia, B. K. Patel, and B. Ollivier, (2000) “Taxonomic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of methanogenic Archaea" Anaerobe 6(4): 205–226. DOI: 10.1006/anae.2000.0345.
- [54] A. Khan, S. Akbar, V. Okonkwo, C. Smith, S. Khan, A. A. Shah, F. Adnan, U. Z. Ijaz, S. Ahmed, and M. Badshah, (2022) “Enrichment of the hydrogenotrophic methanogens for, in-situ biogas up-gradation by recirculation of gases and supply of hydrogen in methanogenic reactor" Bioresource Technology 345: 126219. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126219.
- [55] F. Hu, S. Zhang, X. Wang, C. Wang, J. Wu, L. Xu, G. Xu, and Y. Hu, (2022) “Investigating the role of different materials supplementation in anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste: Performance and microbial commu nity dynamics" Biochemical Engineering Journal 184: 108490. DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2022.108490.
- [56] R. Xu, K. Zhang, P. Liu, A. Khan, J. Xiong, F. Tian, and X. Li, (2018) “A critical review on the interaction of substrate nutrient balance and microbial community structure and function in anaerobic co-digestion" Bioresource Technology 247: 1119–1127. DOI: 10.1016/j. biortech.2017.09.095.
- [57] Q. Yin, Y. Sun, B. Li, Z. Feng, and G. Wu, (2022) “The r/K selection theory and its application in biological wastewater treatment processes" Science of the Total Environment 824: 153836. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153836.
- [58] Y. Deng, M. Liu, T. Fang, H. Ma, I. Beadham, W. Ruan, S. Wang, X. Zhang, and C. Zhang, (2023) “Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of rice straw by amino acid-derived ionic liquid" Bioresource Technology 380: 129076. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129076.
- [59] J. Du, Y. Qian, Y. Xi, and X. Lü, (2019) “Hydrothermal and alkaline thermal pretreatment at mild temperature in solid state for physicochemical properties and biogas production from anaerobic digestion of rice straw" Renewable Energy 139: 261–267. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.097.
- [60] A. B. D. Nandiyanto, N. N. Azizah, and G. C. S. Gir sang, (2022) “Optimal design and techno-economic analysis for corncob particles briquettes: A literature review of the utilization of agricultural waste and analysis calculation" Applied Science and Engineering Progress 15(3): 5508–5508. DOI: 10.14416/j.asep.2021.10.006.