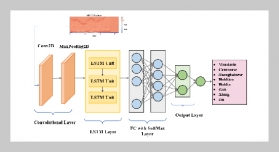
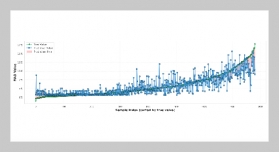
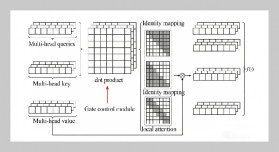
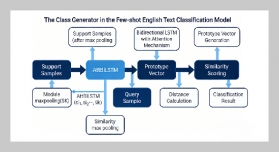
REFERENCES
- [1] Chent, S., Istepaniant, R. H., Whidbornet, J. F. and Wu, J., “Adaptive Simulated Annealing for Designing Finite-Precision PID Controller Structures,” IEE Colloquium on Optimisation in Control: Methods and Applications, pp. 1�3 (1998).
- [2] Kwok, D. P. and Sheng, F., “Genetic Algorithm and Simulated Annealing for Optimal Robot Arm PID Control,” IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation, pp. 707�712 (1994).
- [3] Mitsukura, Y., Yamamoto, T. and Kaneda, M., “A Genetic Tuning Algorithm of PID Parameters,” Inference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Vol. 1, pp. 923� 928 (1997).
- [4] Krohling, R. A., Jaschek, H. and Rey, J. P., “Designing PI/PID Controller for a Motion Control System Based on Genetic Algorithm,” 12th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control,July, pp. 125�130 (1997).
- [5] Davis, L., Handbook of Genetic Algorithms, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York (1991).
- [6] Goldberg, D. E., Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning, Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass (1989).
- [7] Wong, C. C. and Chen, C. C., “A GA-Based Method for Constructing Fuzzy Systems Directly from Numerical Data,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Vol. 30, pp. 904�911 (2000).
- [8] Wong, C.,C., Lin, B. C. and Chen, C. C., “Fuzzy System Design by a GA-Based Method for Data Classification,” Cybernetics and Systems: An International Journal, Vol. 33, pp. 253�270 (2002).
- [9] Wong, C. C., Lin, B. C., Lee, S. A. and Tsai, C. H., “GA-Based Fuzzy System Design in FPGA for an Omni-Directional Mobile Robot,” Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, Vol. 44, pp. 327�347 (2005).
- [10] Kennedy, J. and Eberhart, R., “Particle Swarm Optimization,” IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1942�1948 (1995).
- [11] Shi, Y. and Eberhart, R., “A Modified Particle Swarm Optimizer,” IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, May, pp. 69�73 (1998).
- [12] Angeline, P. J., “Using Selection to Improve Particle Swarm Optimization,” IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, May, pp. 84�89 (1998).
- [13] Shi, Y. and Eberhart, R. C., “Empirical Study of Particle Swarm Optimization,” IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, July, pp. 1945�1950 (1999).
- [14] Clerc, M. and Kennedy, J., “The Particle Swarm � Explosion, Stability, and Convergence in a Multidimensional Complex Space,” IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, Vol. 6, pp. 58�73 (2002).
- [15] Parsopoulous, K. E. and Vrahatis, M. N., ”On the Computation of All Global Minimizers through Particle Swarm Optimization,” IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, Vol. 8, pp. 211�224 (2004).
- [16] Yoshida, H., Kawata, K., Fukuyama, Y. and Nakanishi, Y., “A Particle Swarm Optimization for Reactive Power and Voltage Control Considering Voltage Security Assessment,” IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, Vol. 15, pp. 1232�1239 (2000).
- [17] Gaing, Z. L., “A Particle Swarm Optimization Approach for Optimum Design of PID Controller in AVR System,” IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, Vol. 19, pp. 384�394 (2004).
- [18] Liu, Y., Zhang, J. and Wang, S., “Optimization Design Based on PSO Algorithm for PID Controller,” 5th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Vol. 3, pp. 2419�2422 (2004).
- [19] Eberhart, R. C. and Shi, Y., “Comparison between Genetic Algorithms and Particle Swarm Optimization,” IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, May, pp. 611�616 (1998).
- [20] Shi, X. H., Liang, Y. C., Lee, H. P., Lu, C. and Wang, L. M., “An Improved GA and a Novel PSO-GA-Based Hybrid Algorithm,” Information Processing Letters, Vol. 93, pp. 255�261 (2005).
- [21] Kawabe, T. and Tagami, T., “A Real Coded Genetic Algorithm for Matrix Inequality Design Approach of Robust PID Controller with Two Degrees of Freedom,” 12th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control, July, pp. 119�124 (1997).
- [22] Su, M. C. and Chang, H. T., “A Real-Valued GABased Approach to Extracting Fuzzy Rules for System Identification,” International Joint Conference of CFSA/IFIS/SOFT’ 95 on Fuzzy Theory and Applications, pp. 41�46 (1995).