Chien-Jong Shih This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1, Chi-Nan Yeh2 and Ting-Hao Chang1 1Department of Mechanical and Electro-Mechanical Engineering, Tamkang University, Tamsui, Taiwan 251, R.O.C.
2R&D Center, SanYang Industry, 184 Keng Tzu Kou, Shang Keng Village, Hsin Fong, Taiwan 304, R.O.C.
Received:
December 6, 2010
Accepted:
September 16, 2011
Publication Date:
March 1, 2012
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2012.15.1.03
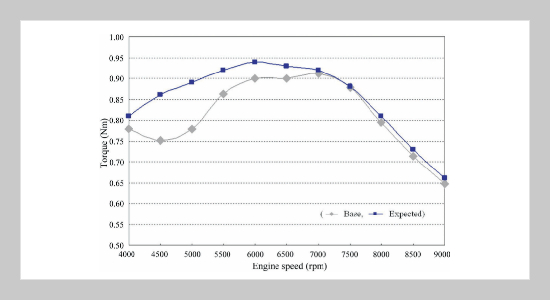
In this paper, the investigation on the effects of intake and exhaust pipeline of a 125 cc small engine motorcycle is presented. The formal design of experiment (DOE) has been utilized to examine the significances of related parameters of pipelines. Four performance functions including the engine torque, fuel consumption, emission of CO and HC have been constructed by response surface methodology (RSM). The weighting strategy of four-objective optimization in six design cases was employed for analysis, comparison, and discussion. After some experimental investigations which provides some useful guidelines for intake and exhaust pipeline design. The proposed integrated process positively enhances the engine torque of overall speed and reduces the fuel consumption. The torque of low range speed can be particularly increased with the methodology presented in this paper. No clear evidence supports the polluted emission can be effectively deducted by modifying the intake pipeline system.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Experimental Optimization, Design of Experiment (DOE), Small Engine, Motorcycle, Mechanical Design
REFERENCES