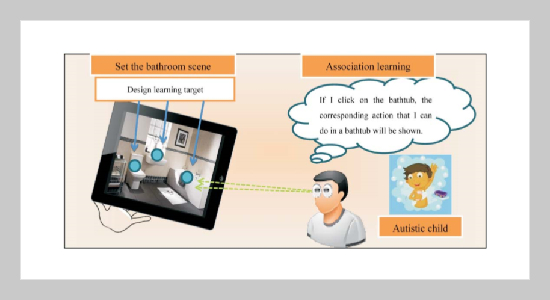
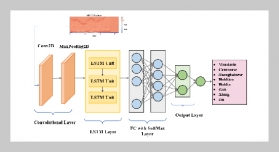
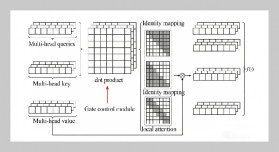
REFERENCES
- [1] Gately, S. E., “Facilitating Reading Comprehension for Students on the Autism Spectrum,” Teaching Exceptional Children, Vol. 40, No. 3, pp. 40�45 (2008).
- [2] Mower, E., Black, M. P., Flores, E., Williams, M. and Narayanan, S., “Rachel: Design of an Emotionally Targeted Interactive Agent for Children with Autism,” 2011 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, pp. 1�6 (2011). doi: 10.1109/ICME.2011. 6011990
- [3] Conn, K., Liu, C., Sarkar, N., Stone, W. and Warren, Z., “Affect-Sensitive Assistive Intervention Technologies for Children with Autism: an Individual-Specific Approach,” IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, pp. 442�447 (2008). doi: 10.1109/ROMAN.2008.4600706
- [4] Cai, Y., Chia, N. K. H., Thalmann, D., Kee, N. K. N., Zheng, J. and Thalmann, N. M., “Design and Development of a Virtual Dolphinarium for Children with Autism,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 208�217 (2013). doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2013.2240700
- [5] Lahiri, U., Bekele, E., Dohrmann, E., Warren, Z. and Sarkar, N., “Design of a Virtual Reality Based Adaptive Response Technology for Children with Autism,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 55�64 (2013). doi: 10. 1109/TNSRE.2012.2218618
- [6] Weilun, L., Elara, M. R. and Garcia, E. M. A., “Virtual Game Approach for Rehabilitation in Autistic Children,” 2011 International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing, pp. 1�6 (2011). doi: 10.1109/ICICS.2011.6174256
- [7] Robins, B., Dautenhahn, K., Te Boekhorst, R. and Billard, A., “Robotic Assistants in Therapy and Education of Children with Autism: Can a Small Humanoid Robot Help Encourage Social Interaction Skills?” Universal Access in the Information Society, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 105�120 (2005). doi: 10.1007/s10209-005- 0116-3
- [8] Bekele, E. T., Lahiri, U., Swanson, A. R., Crittendon, J. A., Warren, Z. E. and Sarkar, N., “A Step Towards Developing Adaptive Robot-Mediated Intervention Architecture (ARIA) for Children with Autism,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 289�299 (2013). doi: 10. 1109/TNSRE.2012.2230188
- [9] Konstantinidis, E. I., Luneski, A., Frantzidis, C. A., Costas, P. and Bamidis, P. D., “A Proposed Framework of an Interactive Semi-Virtual Environment for Enhanced Education of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders,” 22nd IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, pp. 1�6 (2009). doi: 10.1109/CBMS.2009.5255414
- [10] Munson, J. and Pasqual, P., “Using Technology in Autism Research: the Promise and the Perils,” Computer, Vol. 45, No. 6, pp. 89�91 (2012). doi: 10.1109/MC. 2012.220
- [11] Kientz, J. A., Hayes, G. R., Westeyn, T. L., Starner, T. and Abowd, G. D., “Pervasive Computing and Autism: Assisting Caregivers of Children with Special Needs,” IEEE Pervasive Computing, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 28�35 (2007). doi: 10.1109/MPRV.2007.18
- [12] Kozima, H., Nakagawa, C. and Yasuda, Y., “Interactive Robots for Communication-Care: a Case-Study in Autism Therapy,” IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, pp. 341�346 (2005). doi: 10.1109/ROMAN.2005.1513802
- [13] Autismate [Online]. Available: https://itunes.apple.com/ us/app/autismate/id512132428?mt=8.
- [14] Blommaert, A., Philippart, P., Rassaerts, C., Theunissen, E., Widdershoven, S. and Shahid, S., “Day Pad: a Daily Life Assistant for Autistic Children,” Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, pp. 473�474 (2010). doi: 10.1145/1851600.185 1711
- [15] AustimSpace [Online]. Available: https://itunes.apple. com/tw/app/autismspace/id669999 299?l=zh&mt=8.
- [16] Source Code of AustimSpace [Online]. Available: http:// mail.tku.edu.tw/chchou/CILAB/Research_result/Aus timSpace.html.