Madhusudan Singh1, Hakimjon Zaynidinov2, Mastura Zaynutdinova2 and Dhananjay Singh 3 1School of Technology Studies, Endicott College of International Studies, Woosong University, Daejeon, Korea
2Tashkent University of Information Technologies, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3ReSENSE Lab, Department of Electronics Engineering, Hankuk University of Foreign Studies, Yongin, Korea
Received:
November 21, 2018
Accepted:
March 28, 2019
Publication Date:
September 1, 2019
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.201909_22(3).0019
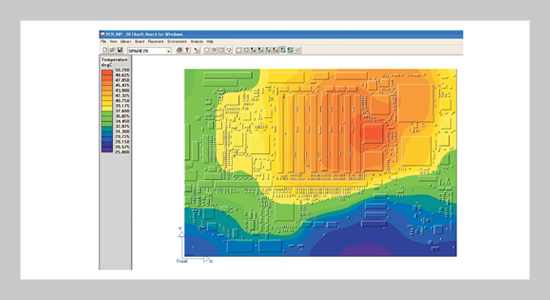
This paper highlights the use of Bi-cubic splines sets for measuring the temperatures at any point (x, y) on printed circuit boards (PCB). This has accomplished by approximating the system of bi-cubic splines of sets of temperatures measured at points on the PCB in a graphical view. The proposed approximation method is using Bi-cubic splines of modeling the temperature field T (x, y) and replace the continuous two variable function by a combination of single variable functions. While developing designs for the navigation and time system (NTS), there is a need for calculating and analyzing the heat generation processes in units in the NTS equipment, which is a factor in choosing design solutions for systems. The boards currently used can conduct full-fledged 3D simulations of heat transfers to PCB which are about 10 percent accurate compared to full-scale tests. It is always difficult to determine the temperatures at specific points on the PCB. Therefore the accurate numbers are only available at the boundaries of temperature zones.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Printed Circuit Board (PCB), Bi-cubic Spline, Thermal Field, Navigation and Time System
REFERENCES