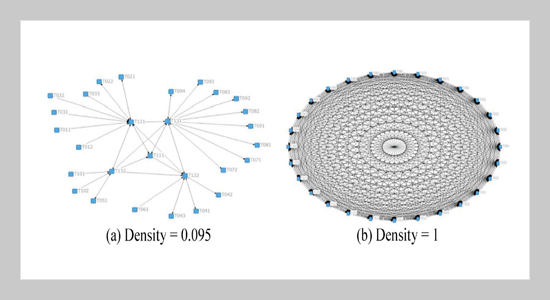
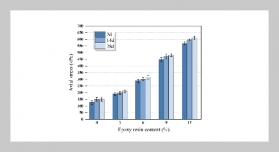
REFERENCES
- [1] Son, J.,andE.M.Rojas(2011)Evolution of collaboration in temporary project teams: an agent-based modeling and simulation approach, J. Constr. Eng. Manage 137(8), 619–628. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.19437862.0000331
- [2] Bertelsen, S. (2003) Construction as a Complex System, presented at the 11th Annual Meeting of the Int.
- [3] Gould, F., and N. Joyce (2009) Construction Project Management. 3rd ED. Pearson Higher.
- [4] Giri, B. E., D. Manongga, and A. Iriani (2014) Using social networking analysis (SNA) to analyze collaboration between students (case study: students of Open University in Kupang), International Journal of Computer Applications 85(1), 39–44. doi: 10.5120/148083022
- [5] Labarbe, E., and D. Thiel (2014) Information sharing to reduce misperceptions of interactions among complementary projects: a multi-agent approach, Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 179(1), 1–9.
- [6] Jin, Y., and R. E. Levitt (1996) The virtual design team: a computational model of project organizations, Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory 2(3), 171–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00127273
- [7] Busi,M., and U.S. Bititci(2006) Collaborative performance management: present gaps and future research, International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management 55(1), 7–25. doi: 10.1108/17410400610 635471
- [8] Horii, T., Jin, Y., and R. E. Levitt (2005) Modeling and analyzing cultural influences on project team performance, Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory 10(4), 305–321. doi: 10.1007/s10588-0056283-1
- [9] Carroll, T., and R. M. Burton (2000) Organizations and complexity:searching for the edge of chaos, Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory 6(4), 319–337. doi: 10.1023/A:1009633728444
- [10] Macal, C. M., and M. J. North (2010) Tutorial on agent-based modelling and simulation, Journal of Simulation 4(3), 151–162. doi: 10.1057/jos.2010.3
- [11] Chinowsky, P., J. Diekmann, and V. Galotti (2008) Social network model of construction, J. Constr. Eng. Manage. 134(10), 804–812. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE) 0733-9364(2008)134:10(804)
- [12] Levitt R. E. (2012) The virtual design team: designing project organizations as engineers design bridges, Journal of Organization Design 1(2), 14–41. doi: 10.1287/ mnsc.45.11.1479
- [13] Park, H., S. H. Han, E. M. Rojas, J. Son, and W. Jung (2011) Social network analysis of collaborative ventures for overseas construction projects, J. Constr. Eng. Manage. 137(5), 344–355. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE) CO.1943-7862.0000301
- [14] Easley, R. F, S. Devaraj, and J. M. Crant (2003) Relating collaborative technology use to teamwork quality and performance: an empirical analysis, Journal of Management Information Systems 19(4), 247–268.
- [15] Love, P. E. D., G. D. Holt, L. Y. Shen, H. Li, and Z. Irani (2002) Using systems dynamics to better understand change and rework in construction project management systems, International Journal of Project Management 20(6), 425–436. doi: 10.1016/S02637863(01)00039-4
- [16] Cheng, M. Y., M. H. Tsai, and Z. W. Xiao (2005) Construction management process reengineering: organizational human resource planning for multiple projects, Automation in Construction 15(6), 785–799. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2005.10.014
- [17] Chang, A. S, F. Y. Shen, and W. Ibbs (2010) Design and construction coordination problems and planning for design–build project new users, Canadian Journal of CivilEngineering 37(12), 1525–1534. doi:10.1139/ L10-090
- [18] Du, J., and M. El-Gafy (2012) Virtual organizational imitation for construction enterprises: agent-based simulation framework for exploring human and organizational implications in construction management,Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering 26(3), 282– 297. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000122
- [19] Wilensky, U., and W. Rand (2015) An introduction to agent-based modeling: modeling natural, social, and engineered complex systems with NetLogo (MITPress), Kindle Edition 68(8). The MITPress, 6484–6485. doi: 10.1063/PT.3.2884
- [20] Rapoport, A. (1953) Spread of information through a population with socio-structural bias: II. Various models with partial transitivity. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 15(4), 535–546. doi: 10.1007/BF02476441
- [21] Levitt, R. E., J. Thomsen, and T. R. Christiansen (1999) Simulating project work processes and organizations: toward a micro-contingency theory of organizational design, Management Science 45(11), 1479–1495. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.45.11.1479
- [22] Fridsma, D. B. (2003) Organizational Simulation of Medical Work: an Information-processing Approach, Stanford University, USA.
- [23] Galbraith J. R. (1984) Organization design: an information processing view, Organizational Effectiveness 8(3), 21–26. doi: 10.1287/inte.4.3.28
- [24] Liben N. D., and J. Kleinberg (2007) The link-prediction problem for social networks, Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 58(7), 1019–1031. doi: 10.1002/asi.20591
- [25] Kossinets, G., and D. J. Watts (2006) Empirical analysis of an evolving social networt, Science 311(5757), 88–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1116869
- [26] Informaton on http://jmvidal.cse.sc.edu/papers/mas.pdf.
- [27] Wilensky, U. (1999) NetLogo, Center for Connected Learning and Computer-Based Modeling Northwestern University, Evanston, IL. Center for Connected Learning and Computer-Based Modeling. Northwestern University, Evanston.
- [28] Xiang, X., R. Kennedy, G. Madey, and S. Cabaniss (2005) Verification and validation of agent-based scientific simulation models, Agent-Directed Simulation Conference 47–55.
- [29] Sargent R. G. (2012) Verification and validation of simulation models. 7(1), 12–24. doi: 10.1057/jos.2012. 20
- [30] Rutkowski, T. M., K. Kakusho, V. Kryssanov, and M. Minoh (2004) Evaluation of the Communication Atmosphere. Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems 3213(53). Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, 364–370. doi: 10.1007/ 978-3-540-30132-5_53