- [1] S. Afzal, B. M. Ziapour, A. Shokri, H. Shakibi, and B. Sobhani, (2023) “Building energy consumption predic�tion using multilayer perceptron neural network-assisted models; comparison of different optimization algorithms" Energy 282: 128446. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128446.
- [2] M. K. Naik, R. Panda, and A. Abraham, (2021) “An entropy minimization based multilevel colour threshold�ing technique for analysis of breast thermograms using equilibrium slime mould algorithm" Applied Soft Com�puting 113: 107955. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107955.
- [3] S. Yin, Q. Luo, and Y. Zhou, (2022) “EOSMA: an equi�librium optimizer slime mould algorithm for engineering design problems" Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 47: 10115–10146. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06513-7.
- [4] H. T. Sadeeq and A. M. Abdulazeez, (2022) “Giant trevally optimizer (GTO): A novel metaheuristic algo�rithm for global optimization and challenging engineer�ing problems" Ieee Access 10: 121615–121640. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3223388.
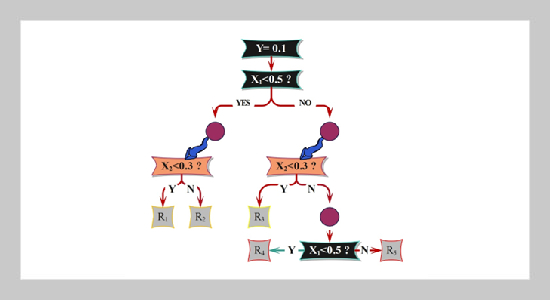
- [5] S. B. Kotsiantis, (2013) “Decision trees: a recent overview" Artificial Intelligence Review 39: 261–283. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-011-9272-4.
- [6] A. Karbassi, B. Mohebi, S. Rezaee, and P. Lestuzzi, (2014) “Damage prediction for regular reinforced concrete buildings using the decision tree algorithm" Computers & Structures 130: 46–56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2013.10.006.
- [7] A. Ahmad, F. Farooq, P. Niewiadomski, K. Ostrowski, A. Akbar, F. Aslam, and R. Alyousef, (2021) “Predic�tion of compressive strength of fly ash based concrete using individual and ensemble algorithm" Materials 14: 794. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040794.
- [8] H. I. Erdal, (2013) “Two-level and hybrid ensembles of decision trees for high performance concrete compressive strength prediction" Engineering Applications of Ar�tificial Intelligence 26: 1689–1697. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2013.03.014.
- [9] R. Chaganti, F. Rustam, T. Daghriri, I. de la Torre Díez, J. L. V. Mazón, C. L. Rodríguez, and I. Ashraf, (2022) “Building heating and cooling load prediction us�ing ensemble machine learning model" Sensors 22: 7692. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197692.
- [10] A. Tsanas and A. Xifara, (2012) “Accurate quantitative estimation of energy performance of residential buildings using statistical machine learning tools" Energy and buildings 49: 560–567. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2012.03.003.
- [11] W. Pessenlehner and A. Mahdavi. Building morphol�ogy, transparence, and energy performance. Citeseer, 2003.
- [12] G. Zhou, H. Moayedi, M. Bahiraei, and Z. Lyu, (2020) “Employing artificial bee colony and particle swarm tech�niques for optimizing a neural network in prediction of heating and cooling loads of residential buildings" Jour�nal of Cleaner Production 254: 120082. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120082.
- [13] H.-J. Wang, T. Jin, H. Wang, and D. Su, (2022) “Appli�cation of IEHO–BP neural network in forecasting building cooling and heating load" Energy Reports 8: 455–465. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.01.216.
- [14] S. Leiprecht, F. Behrens, T. Faber, and M. Finken�rath, (2021) “A comprehensive thermal load forecasting analysis based on machine learning algorithms" Energy Reports 7: 319–326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.08.140.
- [15] F. E. Sapnken, M. M. Hamed, B. Soldo, and J. G. Tamba, (2023) “Modeling energy-efficient building loads using machine-learning algorithms for the design phase" Energy and Buildings 283: 112807. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.112807.
- [16] W. Cai, X. Wen, C. Li, J. Shao, and J. Xu, (2023) “Pre�dicting the energy consumption in buildings using the optimized support vector regression model" Energy 273: 127188. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127188.
- [17] X. Li and R. Yao, (2020) “A machine-learning-based approach to predict residential annual space heating and cooling loads considering occupant behaviour" Energy 212: 118676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118676.
- [18] X. Li and R. Yao, (2020) “A machine-learning-based approach to predict residential annual space heating and cooling loads considering occupant behaviour" Energy 212: 118676. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118676.
- [19] J. Song, L. Zhang, G. Xue, Y. Ma, S. Gao, and Q. Jiang, (2021) “Predicting hourly heating load in a district heat�ing system based on a hybrid CNN-LSTM model" Energy and Buildings 243: 110998. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.110998.
- [20] S. S. Roy, P. Samui, I. Nagtode, H. Jain, V. Shiv�aramakrishnan, and B. Mohammadi-Ivatloo, (2020) “Forecasting heating and cooling loads of buildings: A comparative performance analysis" Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 11: 1253– 1264. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01317-y.
- [21] Q. Zhang, Z. Tian, Y. Ding, Y. Lu, and J. Niu, (2019) “Development and evaluation of cooling load prediction models for a factory workshop" Journal of Cleaner Pro�duction 230: 622–633. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.085.
- [22] E. J. Gago, T. Muneer, M. Knez, and H. Köster, (2015) “Natural light controls and guides in buildings. Energy saving for electrical lighting, reduction of cooling load" Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 41: 1– 13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.08.002.
- [23] A. Shariah, B. Tashtoush, and A. Rousan, (1997) “Cool�ing and heating loads in residential buildings in Jordan" Energy and buildings 26: 137–143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7788(96)01027-4.
- [24] C. Fan, F. Xiao, and Y. Zhao, (2017) “A short-term building cooling load prediction method using deep learn�ing algorithms" Applied energy 195: 222–233. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.064.
- [25] S. Afzal, B. M. Ziapour, A. Shokri, H. Shakibi, and B. Sobhani, (2023) “Building energy consumption predic�tion using multilayer perceptron neural network-assisted models; comparison of different optimization algorithms" Energy 282: 128446. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128446.
- [26] H. Wang, Z. Lei, X. Zhang, B. Zhou, and J. Peng, (2016) “Machine learning basics" Deep learning: 98–164.
- [27] Z. Gao, J. Yu, A. Zhao, Q. Hu, and S. Yang, (2022) “A hybrid method of cooling load forecasting for large commer�cial building based on extreme learning machine" Energy 238: 122073. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.122073.
- [28] Y. Gao, Y. Hang, and M. Yang, (2021) “A cooling load prediction method using improved CEEMDAN and Markov Chains correction" Journal of Building Engi�neering 42: 103041. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103041.
- [29] Y. Ding, Q. Zhang, and T. Yuan, (2017) “Research on short-term and ultra-short-term cooling load prediction models for office buildings" Energy and Buildings 154: 254–267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.08.077.
- [30] M. R. Akbarzadeh, H. Ghafourian, A. Anvari, R. Pourhanasa, and M. L. Nehdi, (2023) “Estimating compressive strength of concrete using neural electromag�netic field optimization" Materials 16: 4200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16114200.
- [31] G. G. Tejani, B. Sadaghat, and S. Kumar, (2023) “Pre�dict the maximum dry density of soil based on individual and hybrid methods of machine learning" Advances in engineering and intelligence systems 2: 98–109. DOI: 10.22034/aeis.2023.414188.1129.
- [32] F. Masoumi, S. Najjar-Ghabel, A. Safarzadeh, and B. Sadaghat, (2020) “Automatic calibration of the ground�water simulation model with high parameter dimensional�ity using sequential uncertainty fitting approach" Water Supply 20: 3487–3501. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.241.
- [33] C. Fan, F. Xiao, and Y. Zhao, (2017) “A short-term building cooling load prediction method using deep learn�ing algorithms" Applied energy 195: 222–233. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.064.
- [34] A. E. Ben-Nakhi and M. A. Mahmoud, (2004) “Cool�ing load prediction for buildings using general regression neural networks" Energy Conversion and Manage�ment 45: 2127–2141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2003.10.009.
- [35] C. Fan, Y. Liao, G. Zhou, X. Zhou, and Y. Ding, (2020) “Improving cooling load prediction reliability for HVAC system using Monte-Carlo simulation to deal with uncer�tainties in input variables" Energy and Buildings 226: 110372. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2020.110372.
- [36] Q. Li, Q. Meng, J. Cai, H. Yoshino, and A. Mochida, (2009) “Applying support vector machine to predict hourly cooling load in the building" Applied Energy 86: 2249–2256. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2008.11.035.
- [37] H. Sha, M. Moujahed, and D. Qi, (2021) “Machine learning-based cooling load prediction and optimal control for mechanical ventilative cooling in high-rise buildings" Energy and Buildings 242: 110980. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.110980.
- [38] L. T. Le, H. Nguyen, J. Dou, and J. Zhou, (2019) “A comparative study of PSO-ANN, GA-ANN, ICA-ANN, and ABC-ANN in estimating the heating load of build�ings’ energy efficiency for smart city planning" Applied Sciences 9: 2630. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132630.
- [39] A. Moradzadeh, A. Mansour-Saatloo, B. Mohammadi-Ivatloo, and A. Anvari-Moghaddam, (2020) “Performance evaluation of two machine learning techniques in heating and cooling loads forecasting of residential buildings" Applied Sciences 10: 3829. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113829.
- [40] T. S. Lim, L. Schaefer, J. T. Kim, and G. Kim, (2012) “Energy benefit of the underfloor air distribution system for reducing air-conditioning and heating loads in buildings" Indoor and Built Environment 21: 62–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X11419345.
- [41] M. A. R. Biswas, M. D. Robinson, and N. Fumo, (2016) “Prediction of residential building energy consumption: A neural network approach" Energy 117: 84–92. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.066.
- [42] A. Shariah, B. Tashtoush, and A. Rousan, (1997) “Cool�ing and heating loads in residential buildings in Jordan" Energy and buildings 26: 137–143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7788(96)01027-4.
- [43] Z.-H. Zhou. Machine learning. Springer nature, 2021.
- [44] M. Gong, Y. Bai, J. Qin, J. Wang, P. Yang, and S. Wang, (2020) “Gradient boosting machine for predicting return temperature of district heating system: A case study for residential buildings in Tianjin" Journal of Building Engineering 27: 100950. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100950.