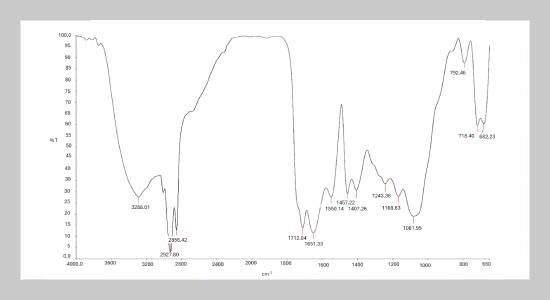
- [1] S. R. P. Primandari, A. A. Islam, Z. Yaakob, and S. Chakrabarty, (2018) “Jatrophacurcas L. biomass waste and its utilization": DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.72803.
- [2] Z. Z. Abidin, N. Ismail, R. Yunus, I. Ahamad, and A. Idris, (2011) “A preliminary study on Jatrophacurcas as coagulant in wastewater treatment" Environmental technology 32(9): 971–977. DOI: 10.1080/09593330.2010.521955.
- [3] Z. Abidin, N. M. Norhafizah Madehi, R. Y. Robiah Yunus, and A. D. Aishah Derahman, (2019) “Effect of storage conditions on Jatropha curcas performance as biocoagulant for treating Palm Oil Mill Effluent." DOI: 10.3923/jest.2019.92.101.
- [4] Y. Ho, I. Norli, A. FM, N. Morad, et al., (2014) “New vegetal biopolymeric flocculant: A degradation and floccu lation study" Iranica Journal of Energy & Environment 5(1): DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ijee.2014.05.01.05.
- [5] S. Katayon, M. M. M. Noor, M. Asma, L. A. Ghani, A. Thamer, I. Azni, J. Ahmad, B. Khor, and A. Suleyman, (2006) “Effects of storage conditions of Moringa oleifera seeds on its performance in coagulation" Biore source technology 97(13): 1455–1460. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2005.07.031.
- [6] W. L. Ang and A. W. Mohammad,(2020) “State of the art and sustainability of natural coagulants in water and wastewater treatment" Journal of Cleaner production 262: 121267. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121267.
- [7] F. Citra, G. Aulia, R. Indiarto, A. Asyifaa, and S. Achmad, (2021) “Conventional And Advanced Food Drying Technology: A Current Review Article" International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research 10(1): 99–107.
- [8] E. H. Mohamed, T. A. Mohammad, M. J. M. M. Noor, and A. H. Ghazali, (2015) “Influence of extraction and freeze-drying durations on the effectiveness of Moringa oleifera seeds powder as a natural coagulant" Desalination and Water Treatment 55(13): 3628–3634. DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2014.946713.
- [9] T. A. Mohammad, E. H. Mohamed, M. J. M. M. Noor, andA.H.Ghazali,(2013) “Coagulation activity of spray dried salt extracted Moringa oleifera" Desalination and Water Treatment 51(7-9): 1941–1946. DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2012.715435.
- [10] M.J. M. M. Noor, E. H. Mohamed, T. A. Mohammad, and A. H. Ghazali, (2013) “Effect of the packaging and storage conditions on the coagulation activity of spray dried salt-extracted Moringa oleifera" Desalination and Water Treatment 51(7-9): 1947–1953. DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2012.715428.
- [11] S. Sayyar, Z. Z. Abidin, R. Yunus, and A. Muhammad, (2009) “Extraction of oil from Jatropha seeds-optimization and kinetics" American Journal of Applied Sciences 6(7): 1390. DOI: 10.3844/ajassp.2009.1390.1395.
- [12] C. Anandharamakrishnan. Handbook of drying for dairy products. John Wiley & Sons, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/9781118930526.CH6.
- [13] M. A. Bezerra, R. E. Santelli, E. P. Oliveira, L. S. Villar, and L. A. Escaleira, (2008) “Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry" Talanta 76(5): 965–977. DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019.
- [14] N.A.A.Halim, Z. Z. Abidin, S. I. Siajam, C. G. Hean, and M. R. Harun, (2021) “Optimization studies and compositional analysis of subcritical water extraction of essential oil from Citrus hystrix DC. leaves" The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 178: 105384. DOI: 10.1016/j.supflu.2021.105384.
- [15] S. Santhalakshmy, S. J. D. Bosco, S. Francis, and M. Sabeena, (2015) “Effect of inlet temperature on physicochemical properties of spray-dried jamun fruit juice pow der" Powder Technology 274: 37–43. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2015.01.016.
- [16] W. Yu, J. Gregory, and L. Campos, (2010) “The effect of additional coagulant on the re-growth of alum–kaolin f locs" Separation and purification technology 74(3): 305–309. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2010.06.020.
- [17] A. P. H. Association, A. W. W. Association, W. P. C. Federation, and W. E. Federation. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 3. American Public Health Association., 1917.
- [18] J. Li, S. Jiao, L. Zhong, J. Pan, and Q. Ma, (2013) “Optimizing coagulation and flocculation process for kaolinite suspension with chitosan" Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 428: 100 110. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.03.034.
- [19] M. Fazaeli, Z. Emam-Djomeh, A. K. Ashtari, and M. Omid, (2012) “Effect of spray drying conditions and feed composition on the physical properties of black mulberry juice powder" Food and bioproducts processing 90(4): 667–675. DOI: 10.1016/j.fbp.2012.04.006.
- [20] P. L. Phing and L. A. K. Saleena, (2022) “Effects of spray-drying parameters on physicochemical properties of powdered fruits" Foods and Raw materials 10(2): 235–251. DOI: 10.21603/2308-4057-2022-2-533.
- [21] N. H. Harun, Z. Zainal Abidin, U. A. Majid, M. R. Abdul Hamid, A. H. Abdullah, R. Othaman, and M. Y. Harun, (2022) “Adopting sustainable jatropha oil bio-based polymer membranes as alternatives for environmental remediation" Polymers 14(16): 3325. DOI: 10.3390/polym14163325.
- [22] N.Kingwatee, A. Apichartsrangkoon, P. Chaikham, S. Worametrachanon, J. Techarung, and T. Pankasem suk, (2015) “Spray drying Lactobacillus casei 01 in lychee juice varied carrier materials" LWT-Food Science and Technology 62(1): 847–853. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2014. 12.007.
- [23] J. Lim, F. Taip, N. Ab Aziz, M. Ibrahim, and M. How, (2021) “Effects of drying methods on the physicochemical properties of powder made from different parts of pump kin" Food Res 5(1): 160–167. DOI: 10.26656/fr.2017.5(S1).058.
- [24] M. V. Zambrano, B. Dutta, D. G. Mercer, H. L. MacLean, and M. F. Touchie, (2019) “Assessment of moisture content measurement methods of dried food products in small-scale operations in developing countries: A review" Trends in Food Science & Technology 88: 484–496. DOI: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.006.
- [25] R. S. Reddy, C. Ramachandra, S. Hiregoudar, U. Nidoni, J. Ram, and M. Kammar, (2014) “Influence of processing conditions on functional and reconstitution properties of milk powder made from Osmanabadi goat milk by spray drying" Small Ruminant Research 119(1-3): 130–137. DOI: 10.1016/J.SMALLRUMRES. 2014.01.013.
- [26] T. Donnellan, T. Hennessy, M. Fenelon, and D. O’Callaghan, (2014) “The potential for scale economies in milk powder processing: anirish case study" International Journal of Dairy Technology 67(1): 129–134. DOI: 10.1111/1471-0307.12109.
- [27] Z. Z. Abidin, N. S. M. Shamsudin, N. Madehi, and S. Sobri, (2013) “Optimisation of a method to extract the active coagulant agent from Jatropha curcas seeds for use in turbidity removal" Industrial Crops and Products 41: 319–323. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.05.003.
- [28] Z.Z.Abidin, N. Madehi, and R. Yunus, (2017) “C oag ulative B ehaviour of Jatropha curcas and its Performance in Wastewater Treatment" Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy 36(6): 1709–1718. DOI: 10.1002/ep.12635.
- [29] E. E. Özdemir, A. Görgüç, E. Gençda˘g, and F. M. Yılmaz, (2022) “Physicochemical, functional and emulsifying properties of plant protein powder from industrial sesame processing waste as affected by spray and freeze drying" Lwt 154: 112646. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112646.
- [30] D. Titus, E. J. J. Samuel, and S. M. Roopan. “Nanopar ticle characterization techniques”. In: Green synthesis, characterization and applications of nanoparticles. Else vier, 2019, 303–319. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-08-102579 6.00012-5.
- [31] J. Xiao, H. Zhang, L. Niu, X. Wang, and X. Lu, (2011) “Evaluation of detoxification methods on toxic and antinutritional composition and nutritional quality of proteins in Jatropha curcas meal" Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 59(8): 4040–4044. DOI: 10.1021/jf200104b.
- [32] A. Mayeen, L. K. Shaji, A. K. Nair, and N. Kalarikkal. “Morphological characterization of nanomaterials”. In: Characterization of nanomaterials. Elsevier, 2018, 335–364. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-08-101973-3.00012-2.
- [33] K. Fyfe, O. Kravchuk, A. V. Nguyen, H. Deeth, and B. Bhandari, (2011) “Influence of dryer type on surface characteristics of milk powders" Drying Technology 29(7): 758–769. DOI: 10.1080/07373937.2010.538481.
- [34] D. Dantas, M. A. Pasquali, M. Cavalcanti-Mata, M. E. Duarte, and H. M. Lisboa, (2018) “Influence of spray drying conditions on the properties of avocado powder drink" Food chemistry 266: 284–291. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.016.
- [35] K. Meftah, S. Meftah, H. Lamkhanter, T. Bouzid, Y. Rezzak, S. Touil, and A. Abid, (2024) “Extraction and optimization of Austrocy lindropuntia subulata powder as a novel green coagulant" Desalination and Water Treatment 318: 100339. DOI: 10.1016/j.dwt.2024.100339.
- [36] B. I. Okolo, O. Adeyi, E. O. Oke, C. M. Agu, P. C. Nnaji, K. N.Akatobi,andD.O.Onukwuli,(2021)“Co agulation kinetic study and optimization using response surface methodology for effective removal of turbidity from paint wastewater using natural coagulants" Scientific African 14: e00959. DOI: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e00959.
- [37] I. Murrieta-Pazos, L. Galet, C. Rolland, J. Scher, and C. Gaiani, (2013) “Interest of energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis to characterize the surface composition of milk powder particles" Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 111: 242–251. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013. 05.025.
- [38] S. Mohd-Asharuddin, N. Othman, N. S. M. Zin, and H. A. Tajarudin. “A chemical and morphological study of cassava peel: A potential waste as coagulant aid”. In: MATEC web of conferences. 103. EDP Sciences. 2017, 06012. DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/201710306012.
- [39] S. Sibartie and N. Ismail. “Potential of Hibiscus sabdarif fa and Jatropha curcas as natural coagulants in the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater”. In: MATEC web of conferences. 152. EDP Sciences. 2018, 01009. DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/201815201009.
- [40] K. A. ADENIRAN and F. Akinwunmi, (2016) “Rel ative Coagulation Effectiveness of Jatropha curcas Press Cake (Physic Nut) and Aluminium Sulphate in Purifying Domestic Sewage" Notulae Scientia Biologicae 8(3): 306–311. DOI: 10.15835/nsb.8.3.9849.
- [41] M. H. Ng and M. S. Elshikh, (2021) “Utilization of Moringa oleifera as natural coagulant for water purification" Industrial and Domestic Waste Management 1(1): 1–11. DOI: 10.53623/idwm.v1i1.41.
- [42] B. M. Kim, H. Lee, and J. Ahn, (2020) “Optimization of initial turbidity and coagulant concentration to remove turbidity using moringa oleifera seed" Journal of Ko rean Society of Environmental Engineers 42(2): 47–54. DOI: 10.4491/KSEE.2020.42.2.47.
- [43] S. Bhatia, Z. Othman, and A. L. Ahmad, (2007) “Pretreatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME)using Moringa oleifera seeds as natural coagulant" Journal of Hazardous Materials 145(1-2): 120–126. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.11.003.
- [44] J. R. Balbinoti, R. M. M. Jorge, R. E. dos Santos Junior, T. C. V. Balbinoti, L. A. de Almeida Coral, and F. de Jesus Bassetti, (2024) “Treatment of low-turbidity water by coagulation combining Moringa oleifera Lam and polyaluminium chloride (PAC)" Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 12(1): 111624. DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111624.