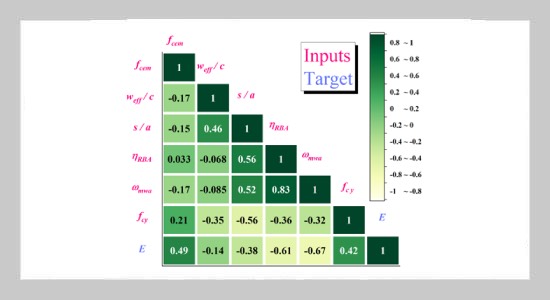
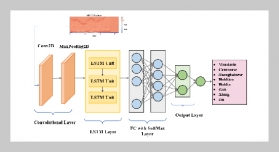
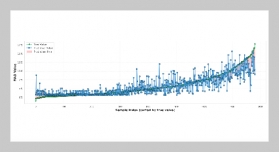
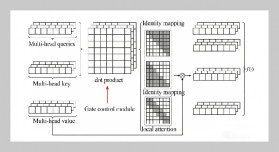
- [1] M.Walczak,(2021)“RopesandKnots: Architectural Emulation in Fifteenth-and Early Sixteenth-Century Central Europe and the Origins of Architecture" source: notes in the history of art 40: 133–142. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1086/714711.
- [2] Y. Cheng and M.Tan, (2018) “The quantitative research of landscape color: A study of Ming Dynasty City Wall in Nanjing" Color Research & Application 43: 436–448. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1002/col.22203.
- [3] , (2018) “Communique of the third national agricultural census":
- [4] S. M. Keown and D. O’Dwyer, (2025) “Enhancing Compressive Strength Prediction in Recycled Aggregate Concrete through Robust Hybrid Machine Learning Approaches" Advances in Engineering and Intelligence Systems 4: 21–37. DOI: 10.22034/aeis.2025.505261.1286.
- [5] E. Hassankhani and M. Esmaeili-Falak, (2024) “Soil–structure interaction for buried conduits influenced by the coupled effect of the protective layer and trench in stallation" Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice 15: 04024012. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1061/JPSEA2.PSENG-1547.
- [6] R. S. Benemaran, M. Esmaeili-Falak, and M. S. Kord lar, (2024) “Improvement of recycled aggregate concrete using glass fiber and silica fume" Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling, Experiments and Design 7: 1895–1914. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1007/s41939-023-00313-2.
- [7] R. Liang and B. Bayrami, (2023) “Estimation of frost durability of recycled aggregate concrete by hybridized Random Forests algorithms" Steel and Composite Structures 49: 91–107. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.12989/scs.2023.49.1.091.
- [8] A.R.T. Khangah, E. Khajavi, H. Azizi, and A. R. A. Novin, (2024) “Radial Basis Function Coupling with Metaheuristic Algorithms for Estimating the Compressive Strength and Slump of High-Performance Concrete" Advances in Engineering and Intelligence Systems 3: 124–142. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.22034/aeis.2024.483670.1241.
- [9] J. Xiao, J. Ying, V. W. Y. Tam, and I. R. Gilbert, (2014) “Test and prediction of chloride diffusion in recycled aggregate concrete" Science China Technological Sciences 57: 2357–2370. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5700-4.
- [10] Guangdong engineering cost information platform. 2022.
- [11] W. Liu, S. Yan, and S. He, (2018) “Landslide damage incurred to buildings: a case study of Shenzhen landslide" Engineering geology 247: 69–83. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.10.025.
- [12] C. L. Wong, K. H. Mo, S. P. Yap, U. J. Alengaram, and T.-C. Ling, (2018) “Potential use of brick waste as alternate concrete-making materials: A review" Journal of cleaner production 195: 226–239. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.193.
- [13] L. Zhu and Z. Zhu, (2020) “Reuse of clay brick waste in mortar and concrete" Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2020: 6326178. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1155/2020/6326178.
- [14] W. Liu, S. Yan, and S. He, (2018) “Landslide damage incurred to buildings: a case study of Shenzhen landslide" Engineering geology 247: 69–83. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.10.025.
- [15] X.Lu,X.Yin,andH.Jiang, (2013) “Shaking table scaled model test on a high-rise building with CFT frame and composite core wall" European journal of environ mental andcivil engineering 17: 616–634. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2013.805435.
- [16] A. Hasan, M. G. Kibria, and F. M. M. Hasan, (2019) “Effects of incorporating recycled brick and stone aggregate as replacement of natural stone aggregate in concrete" Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov 9: 38–48.
- [17] Z. He, A. Shen, H. Wu, W. Wang, L. Wang, and Y. Guo, (2022) “Properties and mechanisms of brick-concrete re cycled aggregate strengthened by compound modification treatment" Construction and Building Materials 315: 125678. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125678.
- [18] S. T. Zhang, (2017) “Experimental study of recycled brick aggregate concrete-filled steel tube columns" Liaoning Univ. Technol.
- [19] A. A. Aliabdo, A. -E. M. Abd-Elmoaty, and H. H. Has san, (2014) “Utilization of crushed clay brick in concrete industry" Alexandria Engineering Journal 53: 151 168. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2013.12.003.
- [20] C. F. Yuan, S. Li, L. Zeng, and Z. Chen, (2018) “Mechanical properties of brick and concrete mixed recycled coarse aggregate concrete" Bulletin of the Chinese Ce ramic Society 37: 398–402.
- [21] M. A. Rashid, M. A. Salam, S. K. Shill, and M. K. Hasan, (2012) “Effect of replacing natural coarse aggregate by brick aggregate on the properties of concrete":
- [22] C. Zheng, C. Lou, G. Du, X. Li, Z. Liu, and L. Li, (2018) “Mechanical properties of recycled concrete with demolished waste concrete aggregate and clay brick aggregate" Results in Physics 9: 1317–1322. DOI: https ://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.04.061.
- [23] W. Chun-he, Z. Ai-liang, J. I. Chang-liang, H. A. N. Jian, and W. Cheng-ming,(2015) “Experimental studies on shear performance of recycled brick coarse aggregate concrete beam" Hydro-science and Engineering: 40 44.
- [24] I. F. S. D. Bosque, W. Zhu, T. Howind, A. Matías, M. I. S. D. Rojas, and C. Medina, (2017) “Properties of interfacial transition zones (ITZs) in concrete containing recycled mixed aggregate" Cement and Concrete Composites 81: 25–34. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.04.011.
- [25] R. S. Benemaran, (2023) “Application of extreme gradient boosting method for evaluating the properties of episodic failure of borehole breakout" Geoenergy Science and Engineering 226: 211837. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211837.
- [26] B. M. Yaychi and M. Esmaeili-Falak, (2024) “Estimating axial bearing capacity of driven piles using tuned random forest frameworks" Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 42: 7813–7834. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1007/s10706-024-02952-9.
- [27] M. Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2024) “Ensemble extreme gradient boosting based models to predict the bearing capacity of micropilegroup" Applied Ocean Research 151: 104149. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2024.104149.
- [28] X. Sun, X. Dong, W. Teng, L. Wang, and E. Has sankhani, (2024) “Creation of regression analysis for estimation of carbon fiber reinforced polymer-steel bond strength" Steel and Composite Structures 51: 509–527. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.12989/scs.2024.51.5.509.
- [29] K. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and B. Razzaghzadeh, (2024) “Application of the optimal fuzzy-based system on bearing capacity of concrete pile" Steel and Composite Structures 51: 25–41. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.12989/scs.2024.51.1.025.
- [30] D. Li, X. Zhang, Q. Kang, and E. Tavakkol, (2023) “Estimation of unconfined compressive strength of marine clay modified with recycled tiles using hybridized extreme gradient boosting method" Construction and Building Materials 393: 131992. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131992.
- [31] R. Derakhshani, M. Zaresefat, V. Nikpeyman, A. GhasemiNejad, S. Shafieibafti, A. Rashidi, M. Ne mati, and A. Raoof, (2023) “Machine learning-based assessment of watershed morphometry in Makran" Land 12: 776. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.3390/land12040776.
- [32] Y. Zhu, L. Huang, Z. Zhang, and B. Bayrami, (2022) “Estimation of splitting tensile strength of modified recycled aggregate concrete using hybrid algorithms" Steel and Composite Structures, An International Journal 44: 389–406.
- [33] M. Esmaeili-Falak, H. Katebi, M. Vadiati, and J. Adamowski, (2019) “Predicting triaxial compressive strength and Young’s modulus of frozen sand using artificial intelligence methods" Journal of Cold Regions Engineering 33: 04019007. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.0000188.
- [34] Y. Dawei, Z. Bing, G. Bingbing, G. Xibo, and B. Razza ghzadeh, (2023) “Predicting the CPT-based pile set-up parameters using HHO-RF and PSO-RF hybrid models" Structural Engineering and Mechanics, An Int’l Journal 86: 673–686.
- [35] M. Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2023) “Ensemble deep learning-based models to predict the resilient modulus of modified base materials subjected to wet-dry cycles" Geomechanics and Engineering 32: 583–600. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.12989/gae.2023.32.6.583.
- [36] M. Esmaeili-Falak and R. S. Benemaran, (2024) “Ap plication of optimization-based regression analysis for evaluation of frost durability of recycled aggregate concrete" Structural Concrete 25: 716–737. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1002/suco.202300566.
- [37] M. H. Nguyen, S. H. Trinh, and H.-B. Ly, (2023) “To ward improved prediction of recycled brick aggregate concrete compressive strength by designing ensemble machine learning models" Construction and Building Mate rials 369: 130613. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130613.
- [38] S.Wang,P.Xia,Z.Wang,T.Meng,andF.Gong,(2023) “Intelligent mix design of recycled brick aggregate concrete based on swarm intelligence" Journal of Building Engineering 71: 106508. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106508.
- [39] T. K. Šipoš, I. Miliˇcevi´c, and R. Siddique, (2017) “Model for mix design of brick aggregate concrete based on neural network modelling" Construction and building materials 148: 757–769. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.111.
- [40] A. Khademi, K. Behfarnia, T. K. Šipoš, and I. Mil iˇcevi´c, (2021) “The use of machine learning models in estimating the compressive strength of recycled brick ag gregate concrete" Computational Engineering and Physical Modeling 4: 1–25. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.22115/cepm.2021.297016.1181.
- [41] L. Bu, G. Du, and Q. Hou, (2021) “Prediction of the compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete based on artificial neural network" Materials 14: 3921. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.3390/ma14143921.
- [42] W. M. Shaban, J. Yang, K. Elbaz, J. Xie, and L. Li, (2021) “Fuzzy-metaheuristic ensembles for predicting the compressive strength of brick aggregate concrete" Re sources, Conservation and Recycling 169: 105443. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105443.
- [43] J. Yang, W. M. Shaban, K. Elbaz, B. S. Thomas, J. Xie, and L. Li, (2020) “Properties of concrete containing strengthened crushed brick aggregate by pozzolan slurry" Construction and Building Materials 247: 118612. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118612.
- [44] S. Rahman, (2017) “Comparison of concrete properties made from recycled brick, virgin brick, and natural stone as coarse aggregates": DOI: http://lib.buet.ac.bd: 8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/4884.
- [45] S. C. Paul, A. J. Babafemi, V. Anggraini, and M. M. Rahman, (2018) “RETRACTED: Properties of Nor mal and Recycled Brick Aggregates for Production of Medium Range (25–30 MPa) Structural Strength Concrete" Buildings 8: 72. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.3390/buildings8050072.
- [46] M. A. Mansur, T. H. Wee, and S. C. Lee, (1999) “Crushed bricks as coarse aggregate for concrete" Mate rials Journal 96: 478–484. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.14359/649.
- [47] P. B. Cachim, (2009) “Mechanical properties of brick aggregate concrete" Construction and Building Mate rials 23: 1292–1297. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.07.023.
- [48] L. J, G. L, and C. L H, (2014) “Experimental research on mechanical behavior of recycled brick coarse aggregate concrete under uniaxial loading" Concrete 6: 78–80.
- [49] Y. Q, (2013) “Study on the preparation methods and the performance of recycled brick aggregate concrete":
- [50] Z. Ai-hua, Z. Ai-liang, H. Jian, W. Cheng-ming, and Q. Yong-guo, (2014) “Experimental Research on Basic Mechanical Properties of Recycled-brick Coarse-aggregate Concrete" Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering: 98–105.
- [51] X. F. Yang, (2018) “Analysis of the force and deformation of recycled brick aggregate concrete components" Tech. Superv. Water Resour. 4: 155–158.
- [52] A. Seyyedabbasi and F. Kiani, (2023) “Sand Cat swarm optimization: A nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems" Engineering with computers 39: 2627–2651. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1007/s00366-022-01604-x.
- [53] W.-Y. Loh, (2011) “Classification and regression trees" Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: data mining and knowledgediscovery1: 14–23. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1002/widm.8.
- [54] D. K. Lim, K. B. Mustapha, and C. P. Pagwiwoko, (2021) “Delamination detection in composite plates using random forests" Composite Structures 278: 114676. DOI: https: //doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114676.
- [55] C. M. Bishop and N. M. Nasrabadi. Patternrecognition and machine learning. 4. Springer, 2006.
- [56] J. Brownlee, (2016) “A gentle introduction to the gradi ent boosting algorithm for machine learning" Machine Learning Mastery 21: