Horng-Jou Wang1, Hsin-Chang Tsai1, Hwang-Kuen Chen1 and Tai-Kang Shing This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.1 1MEMS R&D Department, Research Center, Delta Electronics, Inc. Taoyuan, Taiwan 333, R.O.C.
Received:
March 4, 2005
Accepted:
June 2, 2005
Publication Date:
September 1, 2005
Download Citation:
||https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.2005.8.3.12
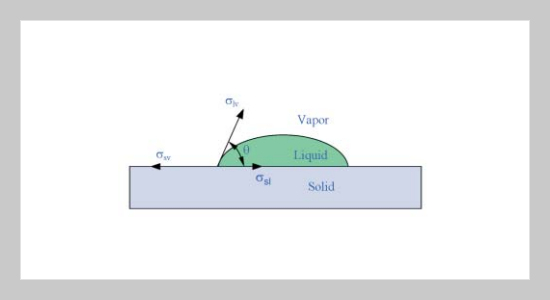
The capillarity of micro grooves with rectangular cross-section is studied theoretically and experimentally in this paper. The Helmholtz free energy method is used to predict the capillarity as the groove is placed vertically and inserted the bottom end into the liquid. In the experiment, micro grooves are first constructed by the thick photoresist patterned by photolithography method and then a thin copper layer is deposited on their surface to improve the hydrophilic property of liquid-solid interface. It is shown that the theoretical and experimental results are in good agreement. Furthermore, the capillary limits of micro grooved heat pipes are investigated. The effects of groove’s width and number on the capillary limit contributed from the maximum capillary pumping pressure and the pressure drops due to the friction and gravitational force are calculated. A workable geometry range of micro grooves for a heat pipe designed to transport a specific heat rate can be determined by these developed tools.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Capillarity, Micro Grooves, Heat Pipes, Capillary Limit
REFERENCES