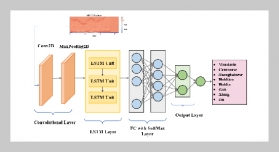
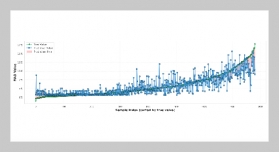
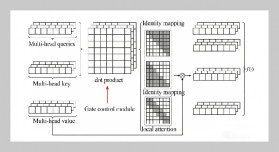
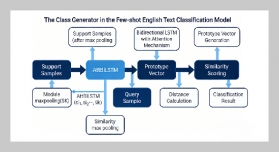
REFERENCES
- [1] Raimondo, M. D. and Gennaro, R., “New Approaches for Deniable Authentication,” Journal of Cryptology, Vol. 22, Issue 4, pp. 572�615 (2009). doi: 10.1007/ s00145-009-9044-3
- [2] Dwork, C., Naor, M. and Sahai, A., “Concurrent Zero-Knowledge,” Proc. of 30th ACM STOC’ 98, Dallas TX, USA, pp. 409-418, (1998). doi: 10.1145/ 276698.276853
- [3] Aumann, Y. and Rabin, M., “Efficient Deniable Authentication of Long Messages,” Presented at International Conference on Theoretical Computer Science in Honor of Professor Manuel Blum’s 60th birthday, (1998). [Online] Available: http://www.cs.cityu.edu. hk/dept/video.html.
- [4] Deng, X., Lee, C.-H. and Zhu, H., “Deniable Authentication Protocols,” IEE Proceeding-Computers and Digital Techniques, Vol. 148, No. 2, pp. 101�104 (2001). doi: 10.1049/ip-cdt:20010207
- [5] Fan, L., Xu, C.-X. and Li, J.-H., “Deniable Authentication Protocol Based on Diffie-Hellman Algorithm,” Electronics Letters, Vol. 38, No. 4, pp. 705�706 (2002). doi: 10.1049/el:20020502
- [6] Naor, M., “Deniable Ring Authentication,” Advances in Cryptology � CRYPTO’02, LNCS 2442, London: Springer-Verlag, pp. 481�498 (2002). doi: 10.1007/ 3-540-45708-9_31
- [7] Shao, Z., “Efficient Deniable Authentication Protocol Based on Generalized ElGamal Signature Scheme,” Computer Standards and Interfaces, Vol. 26, pp. 449�454 (2004). doi: 10.1016/j.csi.2003.11.001
- [8] Lee, W.-B., Wu, C.-C. and Tsaur, W.-J., “A Novel Deniable Authentication Protocol Using Generalized ElGamal Signature Scheme,” Information Sciences, Vol. 177, pp. 1376�1381 (2007). doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2006. 09.020
- [9] Wang, B. and Song, Z.-X., “A Non-Interactive Deniable Authentication Scheme Based on Designated Verifier Proofs,” Information Sciences, Vol. 179, pp. 858�865 (2009). doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2008.11.011
- [10] Hwang, S.-J. and Ma, J.-C., “Deniable Authentication Protocols with Sender Protection,” in 2007 National Computer Symposium (NCS 2007), Wufeng, Taiwan, pp. 762�767 (2007).
- [11] Hwang, S.-J. and Ma, J.-C., “Deniable Authentication Protocols with (Anonymous) Sender Protection,” in 2008 International Computer Symposium (ICS 2008), Tamsui, Taiwan, pp. 412�419 (2008).
- [12] Hwang, S.-J. and Chao, C.-H. “An Efficient Non-Interactive Deniable Authentication Protocol with Anonymous Sender Protection,” in Cryptology and Information Security Conference, Taipei City, Taiwan, R.O.C. (2009).
- [13] Hwang, S.-J. and Chao, C.-H. “Deniable Authentication Protocols with Anonymous Fair Protections,” in Cryptology and Information Security Conference 2010, Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C. (2010).
- [14] Lu, R.-X., Lin, X.-D., Cao, Z.-F., Qin, L.-Q. and Liang, X.-H., “A Simple Deniable Authentication Protocol Based on the Diffie-Hellman Algorithm,” International Journal of Computer Mathematics, Vol. 85, Issue 9, pp. 1315�1323 (2008). doi: 10.1080/00207 160701622741
- [15] Yoon, E.-J. and Yoo, K.-Y., “Secure Deniable Authentication Protocol Based on ElGamal Cryptography,” Networks, Vol. 45, pp. 193�194 (2005). doi: 10.1002/ net.20062
- [16] Hwang, S.-J. and Sung, Y.-H., “Confidential Deniable Authentication Using Promised Signcryption,” Journal of Systems and Software, Vol. 84, Issue 11, pp. 1652�1659 (2011). doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.04.024
- [17] Zheng, Y., “Digital Signcryption or How to Achieve Cost (Signature & Encryption) < Cost (Signature) + Cost (encryption),” Advances in Cryptology � CRYPTO’97, LNCS 1294, New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. 165�179 (1997). doi: 10.1007/BFb0052234
- [18] Nguyen, K., “Asymmetric Concurrent Signatures,” in Proceedings of Information and Communications Security Conference (ICICS 2005), LNCS 3783, New York: Springer Verlag, pp. 181�193 (2005). doi: 10. 1007/11602897_16
- [19] Hwang, S.-J., Sung, Y.-H. and Chi, J.-F., Deniable Authentication Protocols with Confidentiality and Anonymous Fair Protections, Workshop on Cryptography and Information Security, International Computer Symposium 2012 (ICS 2012), National Dong Hwa University, Hualien, Taiwan, Dec. 12�14 (2012).
- [20] Kudla, Caroline J., Special Signature Scheme and Key Agreement Protocols, Ph.D. dissertation, Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham, Surrey, England (2006).
- [21] Schnorr, C. P., “Efficient Identification and Signatures for Smart Cards,” Advances in Cryptology: Proceedings of CRYPTO’ 89, LNCS 435, G. Brassard, Ed., New York: Springer Verlag, pp. 239�252 (1990). doi: 10.1007/0-387-34805-0_22
- [22] Diffie, W. and Hellman, M. E., “New Directions in Cryptography,” IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol. 22, Issue 6, pp. 644�654 (1976). doi: 10.1109/TIT.1976.1055638
- [23] Pointcheval, D. and Stern, J., “Security Arguments for Digital Signatures and Blind Signatures* ,” Journal of Cryptology, Vol. 13, Issue 3, pp. 361�396 (2000). doi: 10.1007/s001450010003
- [24] Chaum, D. and van Antwerpen, H.,“Undeniable Signatures,” Advances in Cryptology: Proceedings of CRYPTO’89, LNCS 435, G. Brassard, Ed., New York: Springer Verlag, pp. 212�216 (1990). doi: 10.1007/ 0-387-34805-0_20
- [25] Ateniese, G., “Efficient Verifiable Encryption (and Fair Exchange) of Digital Signature,” in Proc. of ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS’ 99), ACM Press, New York, U.S.A., pp. 138�146 (1999). doi: 10.1145/319709.319728