- [1] A. Govind, A. C. Thomas, D. Tim, and T . B. Elisabeth, (2011) “Quantifying and modeling post-failure sediment yields from laboratory-scale soil erosion and shallow land slide experiments with silty loess" Geomorphology 129: 49–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.01.012.
- [2] X. Wu.“TheApplication of the Anchor Rod Retaining Wall in Building Slope Research”. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Education, Management, Commerce and Society. 0, 0-0. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.01.012.
- [3] N. Yahui, (2024) “Governance strategies for exposed slopes in ecological management projects" Sichuan Building Materials 50: 64–66. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4011.2024.04.025.
- [4] W. Baojing, H. Xijun, Z. Manle, P. Linyu, and X. Kai heng, (2021) “Research Hotspots and Trend of Green Ecological Network in China Based on Cite Space" Economic Geography 41: 174–183. DOI: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2021.09.018.
- [5] P. Genxing, B. Rongjun, and C. Kun, (2017) “From biowaste treatment to novel bio-material manufacturing: Biomaterial science and technology based on biomass pyrolysis" Science & Technology Review 35: 82–93. DOI: null.
- [6] B. Yaocai, L. Jin, X. Henglin, S. Zezhuo, M. Ke, and D. Yusong, (2023) “Soil stabilization using synthetic polymer for soil slope ecological protection" Engineering Geology 321: 107155–107155. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107155.
- [7] Z. Huaisheng, (2012) “Research on ecological restoration technology for exposed mountains" Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi 03: 21–23. DOI: null.
- [8] L. Shiming, W. Dong, X. Changyou, and T. Jie, (2022) “China’s provincial process CO2 emissions from cement production during 1993–2019" Scientific Data 9: 0-0. DOI: 10.1038/s41597-022-01270-0.
- [9] M. A. Robbie, (2019) “Global CO<sub>2</sub> emissions from cement production, 1928–2018" Earth System Science Data 10: 195–217. DOI: 10.5194/essd-11-1675-2019.
- [10] T.-c. Yan, (2011) “Application of cast-in-place permeable eco-concrete in slope engineering of river course" The Journal of Geology 0: 0-0. DOI: null.
- [11] M. Amanda, V. M. Paula, P. AnaCecília, C. AnaPaula, and J. V. O. Paulo, (2020) “A Review on the Importance of Microbial Biopolymers Such as Xanthan Gum to Improve Soil Properties" Applied sciences 11: 170–170. DOI: 10.3390/app11010170.
- [12] R. Joga Jayaprakash and B. J. S. Varaprasad, (2019) “Sustainable Improvement of Expansive Clays Using Xan than Gum as a Biopolymer" Civil Engineering Journal 5: 1893–1903. DOI: 10.28991/cej-2019-03091380.
- [13] D. Anant Aishwarya, M. Jinesh, K. Ravi, D. Navdeep Kaur, and M. Abhijit, (2023) “Rheological Properties of Xanthan-Gum Solutions and Their Role in Improving River Embankments" Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 0: 0-0. DOI: 10.1007/s10706-023-02678 0.
- [14] W. Juan, T. Zhonggeng, L. Yiming, X. Henglin, and W. Hao, (2023) “Study on the improvement of clay properties by xanthan gum and its application on ecological slope protection engineering" Environmental Technology 0: 1–14. DOI: 10.1080/09593330.2023.2186271.
- [15] Y. Wanli, S. Yuling, M. Pengxue, J. Zhuolong, and C. Yihan, (2022) “An experimental study of the engineering properties and erosion resistance of guar gum reinforced loess" Hydrogeology and Engineering Ge ology 49: 117–124. DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000 3665.202110027.
- [16] J. Zhuolong, Y. Changgen, L. Bo, B. Han, L. Hengx ing, L. Zherui, S. Yuling, and R. Jing, (2023) “Performance test and effect evaluation of guar gum-stabilized loess as a sustainable slope protection material" Journal of Cleaner Production 408: 137085–137085. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137085.
- [17] A. Mohamed, N. Abdelazim, E.-S. Mostafa, and K. Masaki, (2017) “Enhancing mechanical behaviors of collapsible soil using two biopolymers" Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 9: 329 339. DOI: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.11.007.
- [18] T. Thi Phuong An, C. Gye-Chun, and C. Ilhan, (2020) “Water retention characteristics of biopolymer hydrogel containing sandy soils" Hue University Journal of Science: Earth Science and Environment 129: 0-0. DOI: 10.26459/hueuni-jese.v129i4a.5652.
- [19] J. Hyungsoon, S. Haeji, J. Ha-Young, and K. Eunsuk, (2020) “Effects of-glucan and Xanthan gum-based Biopolymers on Plant Growth and Competition in the Riverbank" Ecology and resilient infrastructure 7: 208–217. DOI: 10.17820/eri.2020.7.3.208.
- [20] N.Jing, W. Ziteng, and G. Xueyu, (2020) “Experimental study on the combination of plants and biopolymers for soil solidification" Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 42: 2131–2137. DOI: null.
- [21] X. Xiao Ying, S. Liang, L. Sha, X. Hong, and L. Peng, (2020) “Welan gum promoted the growth of rice seedlings by enhancing carbon and nitrogen assimilation" Carbo hydrate Research 498: 108181–108181. DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2020.108181.
- [22] W. Siwei, Z. Xinxin, Z. Junran, J. Tong, W. Shaokai, Z. Jindi, and M. Zhihao, (2023) “Water retention characteristics and vegetation growth of biopolymer-treated silt soils" Soil and Tillage Research 225: 105544–105544. DOI: 10.1016/j.still.2022.105544.
- [23] S. Feifei, W. Qiang, Z. Xueping, W. Liyu, and Q. Houyuan, (2012) “Study on structure and complex effect of Xanthan gum" Science and Technology of Food Industry 33: 440–443. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2012.07.105.
- [24] S. Qi, Z. Baotang, and Y. Fumin, (2022) “Effects of Xan than Gum and Guar Gumonthe Rheological Properties of Quinoa Juice" Food and Fermentation Science & Technology Technology 58: 64–73. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-506X.2022.03-009.
- [25] B. Katzbauer, (1998) “Properties and applications of xan than gum" Polymer Degradation and Stability 59: 81–84. DOI: 10.1016/s0141-3910(97)00180-8.
- [26] G.-O. Félix, E. S. Victoria, A. C. José, and G. Eduardo Escalante, (2000) “Xanthan gum: production, recovery, and properties" Biotechnology Advances 18: 549–579. DOI: 10.1016/s0734-9750(00)00050-1.
- [27] B. Tinland and R. Marguerite, (1989) “Dependence of the stiffness of the xanthan chain on the external salt concentration" Macromolecules 22: 1863–1865. DOI: 10.1021/ma00194a058.
- [28] L. Zhijia and Y. Ping, (2015) “Injectable thermo responsive hydrogel composed of xanthan gum and methyl cellulose double networks with shear-thinning property" Carbohydrate Polymers 132: 490–498. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.013.
- [29] J. A. M. Carmona, L. Aurora, R. Pablo, C. Nuria, and M. José, (2015) “Nonlinear and linear viscoelastic properties of a novel type of xanthan gum with industrial applications" Rheologica Acta 54: 993–1001. DOI: 10.1007/s00397-015-0888-1.
- [30] K. Werner-Michael, E. Dirk, K. Franziskus, K. Martin, and K. Arne Henning, (1996) “Hydrocolloids and Rheology: Regulation of Visco-elastic Characteristics of Waxy Rice Starch in Mixtures with Galactomannans" Starch Stärke 48: 105–114. DOI: 10.1002/star.19960480307.
- [31] R. Daniela, D. Mariella, and V. Crescenzi, (2005) “Guar gum methyl ethers. Part I. Synthesis and macro molecular characterization" Polymer 46: 12247–12255. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2005.10.083.
- [32] S.Gaurav, S. Shweta, K. Amit, H. A.-M. Ala’a, N. Mu, A. G. Ayman, M. Genene Tessema, and J. S. Florian, (2018) “Guar gum and its composites as potential mate rials for diverse applications: A review" Carbohydrate Polymers 199: 534–545. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018. 07.053.
- [33] G. Wagdi, B. Philippe, T. Béatrice, A. Lina Qadir, and J. E.-G. Abraham, (2022) “Divergent Selection for Seed Ability to Germinate at Extreme Temperatures in Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)" Frontiers in Plant Science 12: 0-0. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.794488.
- [34] Z. Liu, G. Zhifeng, D. Feng, and Z. Xiaojuan, (2014) “Study on Distribution and Mechanical Properties of Plant Roots for Highway Slope Protection in Loess Plateau" Shuitu Baochi Xuebao 28: 66–71. DOI: null.
- [35] R. Sergey, P. Ettore, N. Massimo, and P. Peter, (2018) “An Unexplored Side of Regeneration Niche: Seed Quantity and Quality Are Determined by the Effect of Temperature on Pollen Performance" Frontiers in Plant Science 9: 0-0. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01036.
- [36] X. Mei, C. Ying, L. Jinping, Y. Menghan, and M. Wentao, (2024) “Variation characteristics of soil properties and plant communities along altitude gradients in the Tangjia River Nature Reserve alpine meadow" Chinese Journal of Grassland 46: 97–106. DOI: 10.16742/j. zgcdxb.20240006.
- [37] N.C. Toby and A. J. R. David, (1997) “On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index" Remote Sensing of Environment 62: 241–252. DOI: 10.1016/s0034-4257(97)00104-1.
- [38] H. Shiqin, H. Pengzhi, and S. Xiaoruan, (2021) “Analysis and Research on the Second Maintenance of Hot-in Place Recycling Asphalt Pavemen" Highway 66: 309–314. DOI: null.
- [39] C. Kaisheng, (2018) “Rainfall Erosion Test on Red Clay Slope" Highway Engineering 40: 18–22. DOI: null.
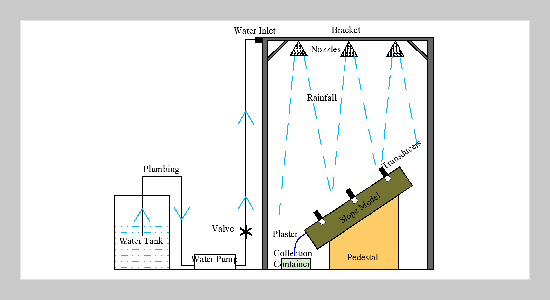
- [40] D. U. Tingting, L. Zhiqing, W. Xiaoming, Y. Bai, D. Qin, C. Wu, and W. Haosen, (2018) “MODEL EXPER IMENT STUDY ON EROSION OF LOESS SLOPE DUETORAINFALL"Journal of Engineering Geol ogy 26: 732–740. DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-252.
- [41] D. Ganeswar and D. Subhraseema, (2022) “Car boxymethyl guar gum: A review of synthesis, properties and versatile applications" European Polymer Journal 176: 111433–111433. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111433.
- [42] C. Rui, Z. Lianyang, and B. Muniram,(2013) “Biopolymer Stabilization of Mine Tailings" Journal of Geotechnical and GeoenvironmentalEngineering139:1802 1807. DOI: 10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000902.
- [43] Q. Ning and W. Xingkui, (1989) “Turbulence Characteristics of Sediment-Laden Flow" Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 115: 781–800. DOI: 10.1061/(asce)0733 9429(1989)115:6(781).