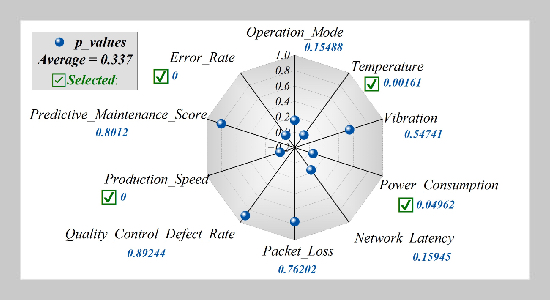
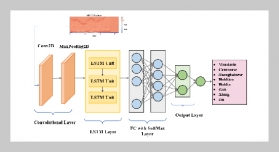
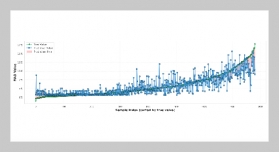
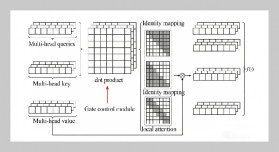
- [1] C. Li, Y. Chen, and Y. Shang, (2022) “A review of industrial big data for decision making in intelligent manufacturing" Engineering science and technology, an international journal 29: 101021. DOI: 10.1016/j.jestch.2021.06.001.
- [2] A. Barari, M. de Sales Guerra Tsuzuki, Y. Cohen, and M. Macchi, (2021) “Intelligent manufacturing systems towards industry 4.0 era" Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 32: 1793–1796. DOI: 10.1007/s10845-021-01769-0.
- [3] Y. Shen and X. Zhang, (2023) “Intelligent manufacturing, green technological innovation and environmental pollution" Journal of Innovation & Knowledge 8: 100384. DOI: 10.1016/j.jik.2023.100384.
- [4] G. Nain, K. K. Pattanaik, and G. K. Sharma, (2022) “Towards edge computing in intelligent manufacturing: Past, present and future" Journal of Manufacturing Systems 62: 588–611. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.01.010.
- [5] L. Zhou, Z. Jiang, N. Geng, Y. Niu, F. Cui, K. Liu, and N. Qi, (2022) “Production and operations management for intelligent manufacturing: A systematic literature re view" International Journal of Production Research 60: 808–846. DOI: 10.1080/00207543.2021.2017055.
- [6] Y. Fu, Y. Hou, Z. Wang, X. Wu, K. Gao, and L. Wang, (2021) “Distributed scheduling problems in intelligent manufacturing systems" Tsinghua Science and Technology 26: 625–645. DOI: 10.26599/TST.2021.9010009.
- [7] M. Attaran, S. Attaran, and B. G. Celik, (2023) “The impact of digital twins on the evolution of intelligent manufacturing and Industry 4.0" Advances in Computational Intelligence 3: 11. DOI: 10.1007/s43674-023 00058-y.
- [8] K. Feng, J. C. Ji, Q. Ni, Y. Li, W. Mao, and L. Liu, (2023) “A novel vibration-based prognostic scheme for gear health management in surface wear progression of the intelligent manufacturing system" Wear 522: 204697. DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2023.204697.
- [9] S. Yin, N. Zhang, K. Ullah, and S. Gao, (2022)“Enhancing digital innovation for the sustainable transformation of manufacturing industry: a pressure-state-response system framework to perceptions of digital green innovation and its performance for green and intelligent manufacturing" Systems 10: 72. DOI: 10.3390/systems10030072.
- [10] B. Wang, F. Tao, X. Fang, C. Liu, Y. Liu, and T. Freiheit, (2021) “Smart manufacturing and intelligent manufacturing: A comparative review" Engineering 7: 738–757. DOI: 10.1016/j.eng.2020.07.017.
- [11] B. He and K.-J. Bai, (2021) “Digital twin-based sustain able intelligent manufacturing: a review" Advances in Manufacturing 9: 1–21. DOI: 10.1007/s40436-020 00302-5.
- [12] H. B. Mahajan, A. Badarla, and A. A. Junnarkar, (2021) “CL-IoT: cross-layer Internet of Things protocol for intelligent manufacturing of smart farming" Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 12: 7777–7791. DOI: 10.1007/s12652-020-02502-0.
- [13] S. WuandJ. Zhang, (2021) “Research on a compound dual innovation capability model of intelligent manufacturing enterprises" Sustainability 13: 12521. DOI: 10.3390/su132212521.
- [14] V. Bortnikova, V. Yevsieiev, I. Botsman, I. Nevliudov, K. Kolesnyk, and N. Jaworski, (2021) “Queries classification using machine learning for implementation in intelligent manufacturing" Publishing House of Bia lystok University of Technology: DOI: 10.24427/978 83-66391-87-1.
- [15] Q. Huang. “Intelligent manufacturing”. In: Springer, 2022, 111–127. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-19-2527-6.
- [16] H.-Y. Zhang, Q.-X. Chen, J. M. Smith, N. Mao, Y. Liao, and S.-H. Xi, (2021) “Queueing network models for intelligent manufacturing units with dual-resource constraints" Computers & Operations Research 129: 105213. DOI: 10.1016/j.cor.2021.105213.
- [17] I. K. Nti, A. F. Adekoya, B. A. Weyori, and O. Nyarko Boateng, (2022) “Applications of artificial intelligence in engineering and manufacturing: a systematic review" Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 33: 1581–1601. DOI: 10.1007/s10845-021-01771-6.
- [18] H. Fan, X. Liu, J. Y. H. Fuh, W. F. Lu, and B. Li, (2025) “Embodied intelligence in manufacturing: lever aging large language models for autonomous industrial robotics" Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 36: 1141–1157. DOI: 10.1007/s10845-023-02294-y.
- [19] H. Yang, L. Li, and Y. Liu, (2022) “The effect of manufacturing intelligence on green innovation performance in China" Technological Forecasting and Social Change 178: 121569. DOI: 10.1016/j.techfore.2022. 121569.
- [20] S. W. Kim, J. H. Kong, S. W. Lee, and S. Lee, (2022) “Recent advances of artificial intelligence in manufacturing industrial sectors: A review" International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing 23: 111 129. DOI: 10.1007/s12541-021-00600-3.
- [21] B.S. A. Alhayani and H. Llhan, (2021) “RETRACTED ARTICLE: Visual sensor intelligent module based image transmission in industrial manufacturing for monitoring and manipulation problems" Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 32: 597–610. DOI: 10.1007/s10845-020-01590-1.
- [22] M. Noor-A-Rahim, F. Firyaguna, J. John, M. O. Khyam, D. Pesch, E. Armstrong, H. Claussen, and H. V. Poor, (2022) “Toward industry 5.0: Intelligent reflecting surface in smart manufacturing" IEEE Communications Magazine 60: 72–78. DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2200016.
- [23] L. Wang, Z. Pan, and J. Wang, (2021) “A review of reinforcement learning based intelligent optimization for manufacturing scheduling" Complex System Modeling and Simulation 1: 257–270. DOI: 10.23919/CSMS.2021.0027.
- [24] H. Yan, X. Du, L. Xu, S. Xu, Y. Zhang, and P. Gong, (2022) “Toward intelligent clothes manufacturing: a systematic method for static and dynamic task allocation by genetic optimization" Neural Computing and Applications 34: 7881–7897. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-022 06890-6.
- [25] X. Zhou, X. Xu, W. Liang, Z. Zeng, S. Shimizu, L. T. Yang, and Q. Jin, (2021) “Intelligent small object detection for digital twin in smart manufacturing with in dustrial cyber-physical systems" IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 18: 1377–1386. DOI: 10.1109/TII.2021.3061419.
- [26] A. Shojaeinasab, T. Charter, M. Jalayer, M. Khadivi, O. Ogunfowora,N.Raiyani,M.Yaghoubi,andH.Na jjaran, (2022) “Intelligent manufacturing execution sys tems: A systematic review" Journal of Manufacturing Systems 62: 503–522. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.01.004.
- [27] J. Wang, C. Xu, J. Zhang, and R. Zhong, (2022) “Big data analytics for intelligent manufacturing systems: A review" Journal of Manufacturing Systems 62: 738 752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.03.005.
- [28] T. Yang, X. Yi, S. Lu, K. H. Johansson, and T. Chai, (2021) “Intelligent manufacturing for the process indus try driven by industrial artificial intelligence" Engineering 7: 1224–1230. DOI: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.04.023.
- [29] H. Wang, Z. Ma, W. Qi, N. Zhang, and H. Zhuang. “A Research Review of the Stacking Classification Model”. In: 2024 6th International Conference on Ma chine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence (MLB DBI). IEEE, 2024, 61–65. DOI: 10.1109/MLBDBI63974.2024.10823722.
- [30] Q. Bi, H. Zhang, and K. Qin, (2021) “Multi-scale stacking attention pooling for remote sensing scene classification" Neurocomputing 436: 147–161. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.038.
- [31] G. Zhao, E. Dougherty, B.-J. Yoon, F. Alexander, and X. Qian, (2021) “Efficient active learning for Gaussian process classification by error reduction" Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: 9734 9746.
- [32] T. Lan, Z. Zhang, J. Sun, W. Zhao, M. Zhang, W. Jia, M. Liu, and X. Guo, (2022) “Regional prediction and prevention analysis of rock burst hazard based on the Gaussian process for binary classification" Frontiers in Earth Science 10: 959232. DOI: 10.3389/feart.2022.959232.
- [33] M. A. Awadallah, M. S. Braik, M. A. Al-Betar, and I. A. Doush, (2023) “An enhanced binary artificial rabbits optimization for feature selection in medical diagnosis" Neural Computing and Applications 35: 20013 20068. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-023-08812-6.
- [34] Y. Wang, Y. Xiao, Y. Guo, and J. Li, (2022) “Dynamic chaotic opposition-based learning-driven hybrid aquila optimizer and artificial rabbits optimization algorithm: framework and applications" Processes 10: 2703. DOI: 10.3390/pr10122703.
- [35] S. N. Makhadmeh, M. A. Al-Betar, M. A. Awadallah, A. K. Abasi, Z. A. A. Alyasseri, I. A. Doush, O. A. Alomari, R. Damaševiˇcius, A. Zajanˇckauskas, and M.A.Mohammed,(2022)“Amodifiedcoronavirus herd immunity optimizer for the power scheduling problem" Mathematics 10: 315. DOI: 10.3390/math10030315.
- [36] A. Hosseinalipour, R. Ghanbarzadeh, B. Arasteh, F. S. Gharehchopogh,andS.Mirjalili,(2024) “Ametaheuris tic approach based on coronavirus herd immunity optimiser for breast cancer diagnosis" Cluster Computing 27: 9451–9475. DOI: 10.1007/s10586-024-04360-3.